Ratio Test Calculator Step By Step
Greels
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
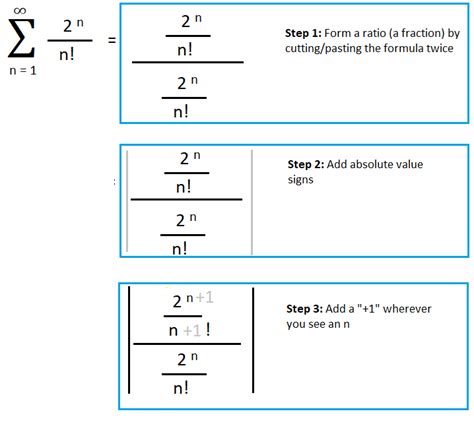
Table of Contents
Ratio Test Calculator: A Step-by-Step Guide to Determining Series Convergence
The ratio test is a powerful tool in calculus used to determine the convergence or divergence of an infinite series. Understanding how to apply the ratio test effectively is crucial for anyone studying calculus or related fields. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the ratio test step-by-step, providing clear explanations, practical examples, and insights into its applications and limitations. We'll also explore how to use a ratio test calculator to streamline the process and avoid common mistakes.
Understanding the Ratio Test
The ratio test examines the ratio of consecutive terms in an infinite series. Formally, for a series denoted as Σa<sub>n</sub>, where a<sub>n</sub> represents the nth term, the ratio test involves calculating the limit:
L = lim (n→∞) |a<sub>n+1</sub> / a<sub>n</sub>|
Based on the value of L, we can determine the convergence or divergence of the series:
- L < 1: The series converges absolutely. This means the series converges, and the absolute values of its terms also converge.
- L > 1: The series diverges.
- L = 1: The test is inconclusive. This means the ratio test doesn't provide enough information to determine convergence or divergence, and other tests need to be applied.
Step-by-Step Application of the Ratio Test
Let's break down the application of the ratio test into manageable steps with illustrative examples.
Step 1: Identify the General Term (a<sub>n</sub>)
The first step is to identify the general term, a<sub>n</sub>, of the given infinite series. This is the expression that represents the nth term of the series.
Example 1: Consider the series Σ (n! / n<sup>n</sup>)
Here, the general term is a<sub>n</sub> = n! / n<sup>n</sup>.
Example 2: Consider the series Σ (2<sup>n</sup> / n!)
Here, the general term is a<sub>n</sub> = 2<sup>n</sup> / n!.
Step 2: Determine a<sub>n+1</sub>
Next, find the expression for a<sub>n+1</sub> by replacing 'n' with 'n+1' in the general term a<sub>n</sub>.
Example 1 (continued): a<sub>n+1</sub> = (n+1)! / (n+1)<sup>(n+1)</sup>
Example 2 (continued): a<sub>n+1</sub> = 2<sup>(n+1)</sup> / (n+1)!
Step 3: Calculate the Ratio |a<sub>n+1</sub> / a<sub>n</sub>|
Now, calculate the absolute value of the ratio a<sub>n+1</sub> / a<sub>n</sub>. This step often involves simplifying the expression using algebraic manipulation and properties of factorials and exponents.
Example 1 (continued):
|a<sub>n+1</sub> / a<sub>n</sub>| = |[(n+1)! / (n+1)<sup>(n+1)</sup>] / [n! / n<sup>n</sup>]|
= |(n+1)! * n<sup>n</sup> / (n+1)<sup>(n+1)</sup> * n!|
= |(n+1) * n<sup>n</sup> / (n+1)<sup>(n+1)</sup>|
= |n<sup>n</sup> / (n+1)<sup>n</sup>|
= |(n/(n+1))<sup>n</sup>| = |(1/(1 + 1/n))<sup>n</sup>|
Example 2 (continued):
|a<sub>n+1</sub> / a<sub>n</sub>| = |[2<sup>(n+1)</sup> / (n+1)!] / [2<sup>n</sup> / n!]|
= |2<sup>(n+1)</sup> * n! / (n+1)! * 2<sup>n</sup>|
= |2 / (n+1)|
Step 4: Evaluate the Limit L = lim (n→∞) |a<sub>n+1</sub> / a<sub>n</sub>|
This is the crucial step. Evaluate the limit of the ratio as n approaches infinity. Remember, the limit determines the convergence or divergence of the series. You might need to apply L'Hôpital's rule or other limit techniques for complex expressions.
Example 1 (continued):
L = lim (n→∞) |(1/(1 + 1/n))<sup>n</sup>| = 1/e (since lim (n→∞) (1 + 1/n)<sup>n</sup> = e)
Since L = 1/e ≈ 0.368 < 1, the series Σ (n! / n<sup>n</sup>) converges.
Example 2 (continued):
L = lim (n→∞) |2 / (n+1)| = 0
Since L = 0 < 1, the series Σ (2<sup>n</sup> / n!) converges.
Step 5: Interpret the Result
Based on the value of L, conclude whether the series converges, diverges, or if the test is inconclusive.
- L < 1: The series converges absolutely.
- L > 1: The series diverges.
- L = 1: The test is inconclusive. Further investigation is needed using other convergence tests (e.g., integral test, comparison test, root test).
Using a Ratio Test Calculator
While performing the ratio test manually provides valuable understanding, a ratio test calculator can significantly simplify the process, especially for complex series. These calculators automate the steps involved, from calculating the ratio to evaluating the limit. They can be particularly helpful in checking your work or handling intricate expressions. However, it is important to understand the underlying principles of the ratio test before relying solely on a calculator. The calculator should be a tool to assist, not replace, your understanding.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incorrect simplification of the ratio: Be meticulous in simplifying the expression |a<sub>n+1</sub> / a<sub>n</sub>|. Errors in simplification can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Misapplication of limit rules: Ensure you correctly apply limit rules and techniques, especially when dealing with indeterminate forms. L'Hôpital's rule can be very useful here.
- Ignoring the absolute value: Remember that the ratio test uses the absolute value of the ratio. Ignoring this can result in incorrect conclusions.
- Misinterpreting the inconclusive case (L=1): If L=1, the ratio test provides no information about the series' convergence or divergence. Don't assume convergence or divergence simply because L=1; other tests are necessary.
Advanced Applications and Limitations of the Ratio Test
The ratio test is a powerful tool, but it has its limitations. It works best for series with terms involving factorials, exponentials, and other functions that lend themselves to simplification. It's less effective for series with complicated trigonometric functions or terms that don't simplify readily.
The ratio test also doesn't always provide a definitive answer, especially when L=1. In such cases, alternative convergence tests, such as the root test, integral test, comparison test, limit comparison test, or alternating series test, might be necessary.
Conclusion
The ratio test is an essential tool for determining the convergence or divergence of infinite series. Understanding its step-by-step application, the interpretation of results, and its limitations is crucial for mastering calculus and related mathematical concepts. While a ratio test calculator can streamline the calculations, a firm grasp of the underlying principles is essential for effective problem-solving and avoiding common errors. By combining a thorough understanding of the theory with the practical application of computational tools, you can confidently determine the convergence or divergence of a wide range of infinite series. Remember to always check your work and consider using multiple methods to confirm your findings.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 90 In
Mar 23, 2025
-
70 Miles An Hour In Kilometers
Mar 23, 2025
-
200 Grams Is How Many Pounds
Mar 23, 2025
-
Polar Equation To Rectangular Equation Converter
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Kilos In 9 Pounds
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Ratio Test Calculator Step By Step . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
