Polar Equation To Rectangular Equation Converter
Greels
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
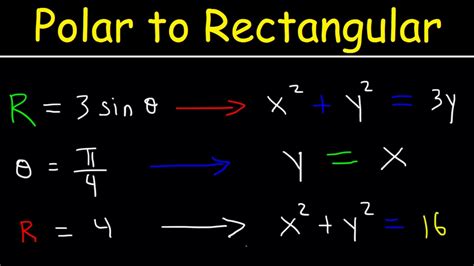
Table of Contents
Polar Equation to Rectangular Equation Converter: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting polar equations to rectangular equations is a fundamental skill in mathematics, particularly in analytic geometry and calculus. Understanding this conversion is crucial for visualizing and analyzing curves expressed in polar coordinates. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process, providing you with a step-by-step approach, helpful examples, and insights into the underlying principles. We will also explore the various scenarios you might encounter and provide you with the tools and understanding to confidently navigate the conversion process.
Understanding Polar and Rectangular Coordinate Systems
Before diving into the conversion process, let's refresh our understanding of the two coordinate systems involved:
Rectangular Coordinates (Cartesian Coordinates)
The rectangular coordinate system, also known as the Cartesian coordinate system, uses two perpendicular axes, the x-axis and the y-axis, to define the location of a point in a plane. A point is represented by an ordered pair (x, y), where x represents the horizontal distance from the origin and y represents the vertical distance from the origin.
Polar Coordinates
The polar coordinate system uses a distance (r) and an angle (θ) to specify the location of a point in a plane. The distance r represents the distance from the origin (pole) to the point, while the angle θ represents the angle (in radians or degrees) measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis to the line segment connecting the origin to the point. A point is represented by an ordered pair (r, θ).
The Conversion Formulas: The Bridge Between Two Worlds
The key to converting between polar and rectangular equations lies in the following fundamental relationships:
- x = r cos θ
- y = r sin θ
- r² = x² + y²
- tan θ = y/x (provided x ≠ 0)
These formulas provide the mathematical bridge between the two coordinate systems. They allow us to express the x and y coordinates in terms of r and θ, and vice versa.
Step-by-Step Guide to Converting Polar Equations to Rectangular Equations
The process of converting a polar equation to a rectangular equation typically involves several steps:
-
Identify the Polar Equation: Begin by clearly identifying the polar equation you wish to convert. This will be an equation expressed in terms of r and θ.
-
Substitute the Conversion Formulas: Substitute the appropriate conversion formulas (x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, r² = x² + y²) into the polar equation. The goal is to replace all instances of r and θ with expressions involving x and y.
-
Simplify the Equation: Simplify the resulting equation using algebraic manipulations. This may involve expanding expressions, factoring, or using trigonometric identities to achieve a simpler form expressed solely in terms of x and y.
-
Solve for y (if possible): If possible, solve the simplified equation for y in terms of x. This form (y = f(x)) is often preferred as it directly represents a function. However, this might not always be feasible, especially for more complex equations.
-
Verify Your Result: Check your final equation to ensure it accurately reflects the original polar equation. You can do this by plotting points or using graphing software to compare the graphs of both equations.
Examples of Polar Equation to Rectangular Equation Conversions
Let's work through some examples to solidify your understanding:
Example 1: Converting r = 5
This polar equation represents a circle with a radius of 5 centered at the origin. Let's convert it to rectangular form:
-
Polar Equation: r = 5
-
Substitution: Since r² = x² + y², we can square both sides of the equation: r² = 25. Substituting r² with x² + y², we get: x² + y² = 25.
-
Simplified Rectangular Equation: x² + y² = 25. This is the equation of a circle with a radius of 5 centered at the origin in rectangular coordinates.
Example 2: Converting r = 2 cos θ
This polar equation represents a circle. Let's convert it:
-
Polar Equation: r = 2 cos θ
-
Substitution: Multiply both sides by r: r² = 2r cos θ. Substitute x = r cos θ and r² = x² + y²: x² + y² = 2x
-
Simplification: Rearrange the equation to the standard form of a circle: x² - 2x + y² = 0. Complete the square for the x terms: (x² - 2x + 1) + y² = 1. This simplifies to (x - 1)² + y² = 1.
-
Rectangular Equation: (x - 1)² + y² = 1. This represents a circle with a radius of 1 centered at (1, 0).
Example 3: Converting r = 2 + 2 cos θ
This polar equation represents a cardioid. The conversion is more involved:
-
Polar Equation: r = 2 + 2 cos θ
-
Substitution: Multiply both sides by r: r² = 2r + 2r cos θ. Substitute x = r cos θ and r² = x² + y²: x² + y² = 2r + 2x.
-
Solving for r: Isolate r: 2r = x² + y² - 2x. Then, r = (x² + y² - 2x) / 2.
-
Substitution and Simplification: Substitute this expression for r back into r² = x² + y²: [(x² + y² - 2x) / 2]² = x² + y². This equation will be quite complex to solve for y explicitly. It's often sufficient to leave the equation in this implicit form. Further simplification can be done by expanding and simplifying the equation, but it remains a complex equation without a straightforward solution for y.
Dealing with More Complex Polar Equations
For more complex polar equations involving trigonometric functions, utilizing trigonometric identities is crucial for successful conversion. These identities can help simplify expressions and ultimately lead to a more manageable rectangular equation. Remember to be patient and methodical in your approach. Often, the final rectangular equation may be implicit rather than explicit (meaning it might not be easily solved for y in terms of x).
Utilizing Online Tools and Software
While manual conversion is crucial for building understanding, numerous online calculators and mathematical software packages (like Mathematica, Maple, or MATLAB) can assist in the conversion process, particularly for complex equations. These tools can provide quick and accurate results, allowing you to check your manual calculations and explore more intricate examples. However, understanding the underlying principles remains paramount.
Applications of Polar to Rectangular Conversions
The ability to convert between polar and rectangular equations has wide-ranging applications in various fields:
- Computer Graphics: Converting equations between coordinate systems is essential in computer graphics for rendering images and creating animations.
- Physics and Engineering: Polar coordinates are often used to describe physical phenomena involving circular motion or radial symmetry, such as planetary orbits or wave propagation. Conversion to rectangular coordinates aids in analysis and visualization.
- Calculus: Converting between coordinate systems simplifies certain integration problems. In some cases, switching to polar coordinates significantly simplifies the calculation of double integrals.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Conversion
Converting polar equations to rectangular equations is a valuable skill that enhances your understanding of coordinate systems and strengthens your problem-solving abilities in mathematics and related fields. By understanding the conversion formulas and applying a systematic approach, you can confidently tackle a wide range of polar equations, even the more complex ones. Remember that practice is key to mastering this process, so work through numerous examples and don't hesitate to utilize available resources to refine your skills. The ability to seamlessly navigate between polar and rectangular representations opens up a world of mathematical possibilities.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Polar Equation To Rectangular Equation Converter . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
