Linear Equation To Standard Form Calculator
Greels
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
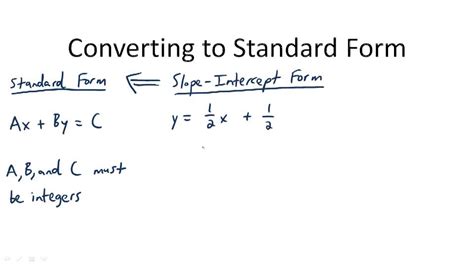
Table of Contents
Linear Equation to Standard Form Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you struggling with converting linear equations into standard form? Do you find yourself spending hours manually manipulating equations, risking errors along the way? Fear not! This comprehensive guide will not only explain the process of converting linear equations to standard form but will also explore the benefits of using a linear equation to standard form calculator, and finally, delve into various related concepts and applications.
Understanding Linear Equations and Standard Form
Before we dive into calculators, let's establish a solid understanding of linear equations and their standard form. A linear equation is an algebraic equation that represents a straight line when graphed. It typically involves one or two variables, usually represented by 'x' and 'y', raised to the power of one.
The standard form of a linear equation is expressed as Ax + By = C, where:
- A, B, and C are integers (whole numbers).
- A is non-negative (A ≥ 0).
- A and B are not both zero.
This form provides a consistent and standardized way to represent linear equations, making them easier to analyze and compare.
Why Convert to Standard Form?
Converting a linear equation to standard form offers several advantages:
- Consistent Representation: Standard form provides a uniform way to represent all linear equations, regardless of their initial format. This simplifies comparisons and analysis.
- Easy Identification of Intercepts: The standard form readily reveals the x-intercept (when y=0) and the y-intercept (when x=0). This is crucial for graphing the equation.
- Simplified Calculations: Standard form often simplifies calculations, particularly when dealing with systems of linear equations. Techniques like elimination are more straightforward when equations are in standard form.
- Foundation for Further Analysis: Standard form serves as a basis for further mathematical analysis, such as finding slopes, determining parallel and perpendicular lines, and solving systems of equations.
Methods for Converting to Standard Form
Several methods exist for converting linear equations into standard form. Let's examine a few common approaches:
1. From Slope-Intercept Form (y = mx + b)
The slope-intercept form, y = mx + b, where 'm' is the slope and 'b' is the y-intercept, is a common way to represent a linear equation. To convert it to standard form (Ax + By = C):
- Move the 'x' term to the left side: Subtract
mxfrom both sides of the equation. This results in-mx + y = b. - Ensure 'A' is non-negative: If 'm' (and therefore '-m') is negative, multiply the entire equation by -1.
- Ensure A, B, and C are integers: Multiply the entire equation by a suitable factor to eliminate any fractions or decimals.
Example: Convert y = 2x - 3 to standard form.
- -2x + y = -3
- 2x - y = 3 (multiplied by -1)
Therefore, the standard form is 2x - y = 3.
2. From Point-Slope Form (y - y₁ = m(x - x₁))
The point-slope form, y - y₁ = m(x - x₁), uses a point (x₁, y₁) on the line and its slope 'm'. The conversion to standard form is similar:
- Distribute 'm': Multiply 'm' by both terms inside the parentheses.
- Move 'x' and 'y' terms to the left side: Add or subtract to get all variables on the left and the constant on the right.
- Ensure A is non-negative and A, B, C are integers: Adjust the equation as needed.
Example: Convert y - 2 = 3(x - 1) to standard form.
- y - 2 = 3x - 3
- -3x + y = -1
- 3x - y = 1 (multiplied by -1)
Therefore, the standard form is 3x - y = 1.
3. From Other Forms
Equations may be presented in other forms, such as those involving fractions or decimals. The process involves similar steps:
- Eliminate fractions: Multiply the entire equation by the least common denominator (LCD) to clear fractions.
- Eliminate decimals: Multiply by powers of 10 to clear decimals.
- Rearrange terms: Move the 'x' term and 'y' term to the left, and the constant to the right.
- Ensure A is non-negative and A, B, C are integers: Adjust accordingly.
The Power of a Linear Equation to Standard Form Calculator
While manual conversion is valuable for understanding the process, using a linear equation to standard form calculator significantly improves efficiency and accuracy, especially when dealing with complex equations or multiple conversions. These calculators automate the conversion process, minimizing the risk of human error, and saving valuable time.
Benefits of using a calculator:
- Speed and Efficiency: Calculators instantly convert equations, saving significant time compared to manual calculations.
- Accuracy: Eliminates errors associated with manual manipulation, ensuring correct results.
- Focus on Interpretation: Frees up time to focus on interpreting the results and applying them to problem-solving.
- Learning Aid: While not a replacement for understanding the process, calculators can be used as a learning tool for checking answers and reinforcing understanding.
Advanced Applications and Related Concepts
Standard form is essential for various mathematical concepts and applications:
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations: Standard form is crucial for using methods like elimination or substitution to solve systems of equations, which represent real-world scenarios involving multiple variables.
- Linear Programming: This optimization technique relies on representing constraints as linear equations in standard form to find optimal solutions.
- Graphing Linear Equations: The x and y intercepts readily available from standard form make graphing much simpler.
- Finding Parallel and Perpendicular Lines: The standard form allows for easy comparison of slopes and intercepts to identify parallel and perpendicular relationships between lines.
- Finding Distance from a Point to a Line: The standard form simplifies the calculation of the distance between a point and a line.
Troubleshooting and Common Mistakes
When converting equations, be mindful of the following:
- Negative Coefficients: Remember to manage negative signs correctly throughout the process.
- Fractions and Decimals: Ensure all coefficients are integers in the final standard form.
- Order of Operations: Follow the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS) accurately.
- Checking Your Work: Always verify your results by substituting values into both the original and standard forms to ensure consistency.
Conclusion
Converting linear equations to standard form is a fundamental skill in algebra. Understanding the underlying principles and mastering the conversion techniques are critical for solving a wide array of problems. While manual conversion builds understanding, the use of a linear equation to standard form calculator significantly improves efficiency and accuracy. By effectively using both manual methods and calculators, you can confidently tackle linear equations and unlock their applications in diverse mathematical contexts. Remember to utilize the calculator as a tool to enhance your learning and efficiency, not as a replacement for fundamental understanding. The more comfortable you become with the process, the more you'll appreciate the power and simplicity of the standard form of a linear equation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
45 Km Is How Many Miles
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Pounds In 58 Kilos
Mar 26, 2025
-
6 5 4 3 2 1
Mar 26, 2025
-
Find The Limit Of The Sequence Calculator
Mar 26, 2025
-
Polar Coordinates To Cartesian Coordinates Calculator
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Linear Equation To Standard Form Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
