Polar Coordinates To Cartesian Coordinates Calculator
Greels
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
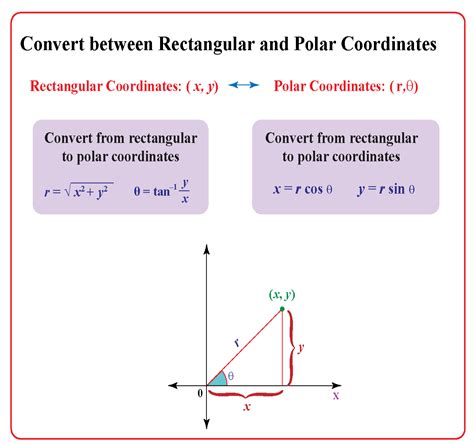
Table of Contents
Polar Coordinates to Cartesian Coordinates Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting between polar and Cartesian coordinate systems is a fundamental task in mathematics, physics, and engineering. While the transformation itself is relatively straightforward, understanding the underlying principles and having access to the right tools can significantly enhance efficiency and accuracy. This article delves into the intricacies of converting polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates, offering a comprehensive guide that includes the mathematical formulas, practical applications, and a detailed exploration of using a polar to Cartesian coordinates calculator.
Understanding Coordinate Systems
Before diving into the conversion process, it's crucial to grasp the fundamental differences between the two coordinate systems:
Cartesian Coordinates (Rectangular Coordinates)
Cartesian coordinates, also known as rectangular coordinates, represent a point in a two-dimensional plane using two perpendicular axes: the x-axis (horizontal) and the y-axis (vertical). A point is uniquely defined by its x and y values, written as an ordered pair (x, y). The origin (0, 0) is the point where the two axes intersect.
Polar Coordinates
Polar coordinates represent a point using a distance and an angle. The distance, denoted by r, is the straight-line distance from the origin to the point. The angle, denoted by θ (theta), is the angle formed between the positive x-axis and the line connecting the origin to the point, measured counter-clockwise. A point in polar coordinates is represented as (r, θ).
The Conversion Formulas
The conversion between polar and Cartesian coordinates relies on simple trigonometric relationships. To convert from polar coordinates (r, θ) to Cartesian coordinates (x, y), we use the following formulas:
- x = r * cos(θ)
- y = r * sin(θ)
These formulas leverage the definitions of cosine and sine in a right-angled triangle where r is the hypotenuse, x is the adjacent side, and y is the opposite side.
Practical Applications
The conversion between polar and Cartesian coordinates finds numerous applications across various fields:
1. Graphics and Game Development
In computer graphics and game development, polar coordinates are often used to define the position and movement of objects, particularly in situations involving circular or radial patterns. Converting these polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates is essential for rendering the objects on a screen using a rectangular pixel grid. For example, designing a circular projectile trajectory in a game often starts with polar coordinates defining the distance and angle of the projectile, later converted to Cartesian coordinates for precise positioning.
2. Robotics and Automation
Robotics extensively utilizes coordinate systems to control the movement and positioning of robotic arms. Defining the desired position of the robotic arm using polar coordinates (e.g., distance from the base and angle of the arm) is often more intuitive and simplifies programming. Converting these polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates is crucial for providing the necessary instructions to the robotic control system.
3. Physics and Engineering
Many physical phenomena, such as projectile motion, wave propagation, and electric fields, are more easily described using polar coordinates. However, calculations and simulations frequently require Cartesian coordinates. The conversion between these systems is therefore vital for solving problems in physics and engineering. For example, modeling the trajectory of a rocket often begins with polar coordinates, but simulations requiring precise calculations of position and velocity rely on Cartesian coordinates.
4. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS systems often use both Cartesian and polar coordinate systems. While Cartesian coordinates are used for mapping locations on a flat plane, polar coordinates are helpful for representing locations relative to a central point, such as a radar station or a weather monitoring center. Converting between these systems is important for data integration and analysis.
5. Signal Processing
In signal processing, polar coordinates are used to represent signals in the frequency domain. The magnitude and phase of a signal are often represented as polar coordinates. Converting to Cartesian coordinates allows for linear algebraic manipulation and analysis of signals.
Using a Polar to Cartesian Coordinates Calculator
While the conversion formulas are straightforward, manually calculating them, especially for numerous points, can be tedious and error-prone. This is where a polar to Cartesian coordinates calculator becomes invaluable. These calculators streamline the process, providing quick and accurate conversions.
Key Features to Look For in a Calculator:
- Input Fields: Clear and intuitive input fields for entering the polar coordinates (r and θ). The calculator should accept various angle input formats (degrees, radians).
- Output Display: A clear display of the calculated Cartesian coordinates (x and y).
- Multiple Calculations: The ability to perform multiple conversions without having to re-enter the inputs each time.
- Error Handling: Robust error handling to prevent issues with invalid inputs (e.g., negative radius).
- Unit Selection: Ability to choose between degrees and radians for the angle input.
Steps for Using a Calculator:
- Input the Polar Coordinates: Enter the value of r (radius) and θ (angle) into the designated input fields. Ensure you select the correct unit for the angle (degrees or radians).
- Select Calculation Mode: If the calculator offers different modes, select the "Polar to Cartesian" mode.
- Perform Calculation: Click the "Calculate" or equivalent button to initiate the conversion.
- Review the Output: The calculator will display the calculated Cartesian coordinates (x, y).
Advanced Considerations and Potential Challenges
While the basic conversion is straightforward, some scenarios require additional considerations:
-
Handling Negative Radii: While the radius r is typically non-negative, some applications might use negative radii to represent points in the opposite direction. A robust calculator should handle both positive and negative radii correctly. Note that a negative radius will reflect the point across the origin.
-
Angle Representation: Angles can be represented in degrees or radians. Always ensure you are using the correct units for both input and output. The calculator should ideally provide clear indication and flexibility.
-
Dealing with Angles Outside the Standard Range: Angles greater than 360° (2π radians) or negative angles should be handled correctly by wrapping around to equivalent angles within the standard range (0° to 360° or 0 to 2π radians).
-
Accuracy and Precision: The calculator's accuracy depends on the underlying algorithms and the precision of the trigonometric functions used.
Conclusion
Converting polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates is a fundamental operation with wide-ranging applications across various disciplines. Understanding the underlying mathematical principles and utilizing a reliable polar to Cartesian coordinates calculator can significantly enhance efficiency and accuracy in solving problems involving these coordinate systems. By selecting a calculator with appropriate features and understanding potential challenges, users can confidently and efficiently handle coordinate transformations. Remember to always double-check the results, particularly for critical applications. The availability of accurate and easy-to-use calculators makes this essential mathematical conversion process efficient and accessible to everyone.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Pounds Is 89 Kilograms
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Much Is 117 Pounds In Kg
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Big Is 21 Cm In Inches
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Kilos Is 117 Pounds
Mar 29, 2025
-
Volume Of Revolution Calculator Y Axis
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Polar Coordinates To Cartesian Coordinates Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
