Find The Product Simplify Your Answer
Greels
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
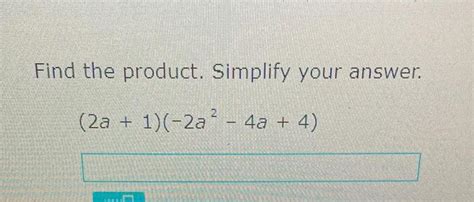
Table of Contents
Find the Product: Simplify Your Answer – A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Multiplication
Multiplication, at its core, is repeated addition. While seemingly simple, mastering multiplication, especially when dealing with larger numbers or complex expressions, requires understanding strategies for simplification and efficiency. This comprehensive guide explores various techniques to find the product and simplify your answer, applicable to diverse mathematical scenarios.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Properties of Multiplication
Before diving into advanced simplification techniques, let's solidify our understanding of the fundamental properties governing multiplication:
1. Commutative Property:
The order of factors doesn't affect the product. This means a x b = b x a. For example, 5 x 3 = 3 x 5 = 15. This property is immensely useful for rearranging numbers to facilitate easier calculations.
2. Associative Property:
The grouping of factors doesn't alter the product. This means (a x b) x c = a x (b x c). For example, (2 x 5) x 4 = 2 x (5 x 4) = 40. This allows us to strategically group numbers for simpler multiplication.
3. Distributive Property:
This property links multiplication and addition. It states that a x (b + c) = (a x b) + (a x c). For instance, 3 x (4 + 2) = (3 x 4) + (3 x 2) = 12 + 6 = 18. This is crucial for simplifying expressions involving parentheses.
4. Identity Property:
Any number multiplied by 1 remains unchanged. This means a x 1 = a. This property might seem basic, but it’s fundamental to many simplification steps.
5. Zero Property:
Any number multiplied by 0 equals 0. This means a x 0 = 0. This is a crucial property for identifying expressions that simplify to zero.
Simplifying Multiplication: Techniques and Strategies
Mastering simplification requires a toolbox of strategies. Let's delve into some key techniques:
1. Prime Factorization:
Breaking down numbers into their prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves) significantly simplifies multiplication. For instance, consider 12 x 15. The prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3, and for 15 it's 3 x 5. Therefore, 12 x 15 = (2 x 2 x 3) x (3 x 5) = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 5 = 180. This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers.
2. Exponent Rules:
When multiplying numbers with exponents, remember that a<sup>m</sup> x a<sup>n</sup> = a<sup>m+n</sup>. This means you add the exponents when the base is the same. For example, 2<sup>3</sup> x 2<sup>2</sup> = 2<sup>3+2</sup> = 2<sup>5</sup> = 32. Understanding exponent rules is crucial for simplifying algebraic expressions and large numerical calculations.
3. Cancellation:
When multiplying fractions, you can cancel common factors from the numerator and denominator. For example, (12/15) x (5/6) can be simplified by canceling out a 3 from 12 and 6, and a 5 from 15 and 5, resulting in (4/3) x (1/1) = 4/3 or 1 1/3.
4. Using Distributive Property for Simplification:
The distributive property is a powerful tool for simplifying expressions involving parentheses. Consider 5 x (12 + 8). Instead of adding 12 and 8 first (which is simpler in this case), applying the distributive property gives 5 x 12 + 5 x 8 = 60 + 40 = 100. While this example seems straightforward, the distributive property becomes invaluable when dealing with more complex algebraic expressions.
5. Mental Math Strategies:
Developing mental math skills is essential for quick and efficient multiplication. Techniques like breaking down numbers, using rounding, and employing known multiplication facts significantly improve calculation speed and accuracy. For example, to multiply 98 by 7, you can think of it as (100 - 2) x 7 = (100 x 7) - (2 x 7) = 700 - 14 = 686.
Advanced Simplification: Dealing with Complex Expressions
Beyond basic numerical multiplication, simplification extends to complex algebraic expressions and equations. Here are advanced strategies:
1. Factorization in Algebra:
Factorization involves expressing an algebraic expression as a product of simpler expressions. This is crucial for solving equations, simplifying fractions, and simplifying complex expressions. For example, x² + 5x + 6 can be factored into (x + 2)(x + 3).
2. Combining Like Terms:
In algebraic expressions, combining like terms involves simplifying by adding or subtracting terms with the same variables and exponents. For example, 3x² + 5x + 2x² - x simplifies to 5x² + 4x.
3. Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS):
Remember the order of operations: Parentheses/Brackets, Exponents/Orders, Multiplication and Division (from left to right), Addition and Subtraction (from left to right). This ensures consistent and accurate simplification of complex expressions. For instance, 2 + 3 x (4 + 2) / 2 – 1 is solved as follows: 2 + 3 x 6 / 2 -1 = 2 + 18/2 -1 = 2 + 9 - 1 = 10.
4. Working with Fractions and Decimals:
Simplify fractions by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator. Convert decimals to fractions for easier multiplication in some cases. For example, 0.5 x 0.25 is equivalent to (1/2) x (1/4) = 1/8.
5. Simplifying Radicals:
Simplify radicals by factoring out perfect squares. For example, √12 simplifies to √(4 x 3) = 2√3.
Practical Applications and Problem-Solving
The ability to find the product and simplify efficiently has broad applications in various fields:
-
Everyday Calculations: From calculating grocery bills to determining unit prices, simplification skills are crucial in daily life.
-
Finance and Accounting: Calculating interest, taxes, and profits heavily relies on accurate and efficient multiplication and simplification.
-
Engineering and Physics: Many engineering and physics problems involve complex calculations that require simplification for accurate solutions.
-
Computer Science: Efficient algorithms for multiplication and simplification are essential for optimizing computer programs.
-
Data Analysis: Simplifying large datasets through multiplication and summation operations is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions.
Tips for Success in Multiplication and Simplification
-
Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to mastering multiplication and simplification techniques.
-
Break Down Complex Problems: Divide large or complex problems into smaller, more manageable steps.
-
Use Visual Aids: Diagrams and other visual aids can help visualize and understand complex multiplication problems.
-
Check Your Work: Always check your answer to ensure accuracy.
-
Utilize Technology Wisely: Calculators and online tools can assist with complex calculations, but understanding the underlying principles is still crucial.
Mastering multiplication and simplification is a journey, not a destination. Consistent effort, a strategic approach, and a solid understanding of fundamental principles will equip you with the skills to tackle any multiplication problem efficiently and accurately. By utilizing the techniques discussed in this guide, you can significantly enhance your mathematical abilities and apply them effectively in various aspects of life and work.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Miles Is 160 Km
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 800 M
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 5 Percent Of 2000
Mar 26, 2025
-
Partial Derivative Calculator X Y Z
Mar 26, 2025
-
Express In Simplest Form With A Rational Denominator
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Find The Product Simplify Your Answer . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
