Area Of The Shaded Region Calculator
Greels
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
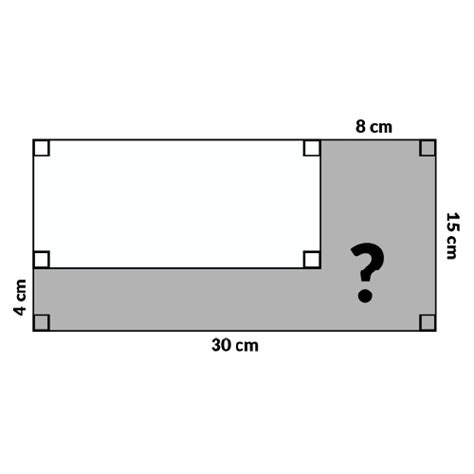
Table of Contents
Area of the Shaded Region Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Calculating the area of shaded regions is a common problem in geometry, appearing frequently in math classes, standardized tests, and real-world applications. While seemingly simple, these problems can quickly become complex depending on the shapes involved. This comprehensive guide will explore various methods for calculating the area of shaded regions, covering a range of shapes and complexity levels. We'll also delve into the importance of using an area of the shaded region calculator, and provide you with the knowledge to confidently tackle these problems.
Understanding the Basics: Area Formulas
Before we dive into shaded regions, let's refresh our understanding of basic area formulas for common shapes:
1. Rectangle:
- Formula: Area = length × width
- Symbol: A = l × w
2. Square:
- Formula: Area = side × side or side²
- Symbol: A = s²
3. Triangle:
- Formula: Area = (1/2) × base × height
- Symbol: A = (1/2)bh
4. Circle:
- Formula: Area = π × radius²
- Symbol: A = πr²
5. Trapezoid:
- Formula: Area = (1/2) × (sum of parallel sides) × height
- Symbol: A = (1/2)(b₁ + b₂)h
Calculating the Area of Shaded Regions: Techniques and Strategies
The key to calculating the area of a shaded region is to break down the problem into smaller, manageable parts. This often involves subtracting the area of one shape from another, or adding the areas of several shapes together. Let's explore some common scenarios:
1. Shaded Region within a Rectangle:
Imagine a rectangle with a smaller circle or square inside. To find the shaded area (the area of the rectangle excluding the inner shape), follow these steps:
- Calculate the area of the outer shape (rectangle): Use the formula A = l × w.
- Calculate the area of the inner shape (circle or square): Use the appropriate formula (A = πr² for a circle or A = s² for a square).
- Subtract the area of the inner shape from the area of the outer shape: Shaded Area = Area(rectangle) - Area(inner shape).
Example: A rectangle has length 10 cm and width 5 cm. A circle with a radius of 2 cm is inside the rectangle.
- Area of rectangle = 10 cm × 5 cm = 50 cm²
- Area of circle = π × (2 cm)² ≈ 12.57 cm²
- Shaded area = 50 cm² - 12.57 cm² ≈ 37.43 cm²
2. Overlapping Shapes:
When shapes overlap, finding the shaded region often requires more intricate calculations. Consider two overlapping circles. To find the area of the overlapping region, you might need to use trigonometry or calculus depending on the complexity of the overlap. However, for simpler cases, you can use the following approach:
- Calculate the area of each shape individually.
- Calculate the area of the intersection (the overlapping region). This often requires breaking down the intersection into smaller, manageable shapes.
- Add the areas of the individual shapes and subtract the area of the intersection twice to avoid double-counting the overlap. Shaded Area = Area(Shape 1) + Area(Shape 2) - 2 * Area(Intersection)
This method is most effective when the intersection can be easily described as a simpler shape (like a rectangle or triangle).
3. Shaded Regions with Irregular Shapes:
For irregularly shaped shaded regions, approximation techniques may be necessary. These techniques involve breaking the irregular shape into smaller, more regular shapes (rectangles, triangles, etc.) and approximating the area of the irregular shape by summing the areas of the smaller shapes. This is often done using numerical integration methods if higher accuracy is required.
The Importance of an Area of the Shaded Region Calculator
While understanding the underlying mathematical principles is crucial, using an area of the shaded region calculator can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy. Calculators can handle complex calculations quickly and accurately, minimizing the risk of human error, particularly with intricate shapes or multiple overlapping regions. Furthermore, a good calculator will often provide a step-by-step breakdown of the calculations, helping you learn the process even as it assists with the computation.
Choosing the Right Calculator: Features to Look For
When selecting an area of the shaded region calculator, consider the following features:
- Versatility: Can it handle various shapes, including circles, triangles, rectangles, and irregular shapes?
- Accuracy: Does it provide accurate results, especially for complex calculations?
- Ease of Use: Is the interface intuitive and easy to navigate?
- Step-by-Step Solutions: Does it provide detailed steps to show how the calculation is performed? This is invaluable for learning purposes.
- Visual Aids: Does it offer graphical representations of the shapes and shaded regions? Visual aids can greatly enhance understanding.
Beyond Basic Calculations: Advanced Techniques
For advanced problems involving more complex shapes or unusual overlaps, more advanced mathematical techniques may be necessary. These could include:
- Calculus (Integration): Used for finding areas under curves and for irregularly shaped regions that cannot be easily decomposed into simpler shapes.
- Coordinate Geometry: Useful for finding areas of regions defined by equations.
- Numerical Methods: Approximation techniques used for solving problems where exact solutions are difficult or impossible to obtain.
Real-World Applications
Calculating shaded regions is not just a mathematical exercise. It has numerous real-world applications, including:
- Engineering: Calculating the area of cross-sections in structural design.
- Architecture: Determining the amount of material needed for various construction projects.
- GIS (Geographic Information Systems): Estimating the area of land parcels, forests, or other geographical features.
- Computer Graphics: Rendering complex scenes and objects.
Conclusion
Calculating the area of a shaded region can range from straightforward to incredibly challenging. Understanding the basic formulas and techniques, coupled with the strategic use of an area of the shaded region calculator, allows you to efficiently and accurately solve a wide range of problems. Remember to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable parts, and consider using advanced techniques when necessary. By mastering these methods, you will not only excel in your mathematical studies but also gain valuable skills applicable to diverse real-world scenarios. Don't hesitate to explore various calculators and find one that best fits your needs and learning style. The more you practice, the more proficient you'll become at tackling these often-complex geometric problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
96 In Is How Many Feet
Mar 24, 2025
-
Multiply And Divide Rational Expressions Solver
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is 22 Cm In Inches
Mar 24, 2025
-
Multiply And Divide Rational Expressions Calculator
Mar 24, 2025
-
110 Pounds Is How Many Kilograms
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Area Of The Shaded Region Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
