Multiply And Divide Rational Expressions Calculator
Greels
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
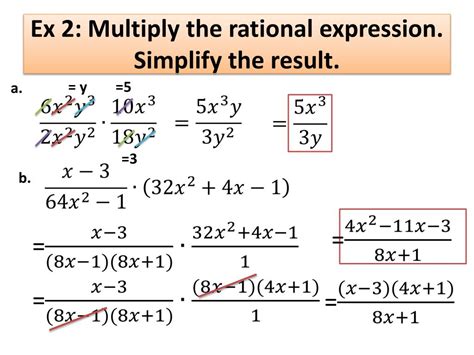
Table of Contents
Multiply and Divide Rational Expressions Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Rational expressions, the algebraic equivalent of fractions, can be tricky to manipulate. Multiplying and dividing them requires a keen understanding of factoring, simplification, and identifying restrictions. While the process is straightforward once mastered, the potential for errors is high, especially with complex expressions. This is where a multiply and divide rational expressions calculator can be invaluable. This guide explores the intricacies of rational expression manipulation, the advantages of using a calculator, and provides a comprehensive walkthrough of the process, demonstrating how to use such a tool effectively.
Understanding Rational Expressions
Before diving into the mechanics of multiplication and division, let's solidify our understanding of rational expressions. A rational expression is simply a fraction where the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example:
- (3x² + 2x)/(x - 1) is a rational expression.
- (x² + 5x + 6) / (x² - 4) is also a rational expression.
Key Characteristics:
- Polynomials: The numerator and denominator must be polynomials – expressions involving variables raised to non-negative integer powers.
- Undefined Values: Rational expressions are undefined when the denominator equals zero. Identifying these restrictions is crucial. These restrictions represent values of the variable that make the denominator zero, and hence, the entire expression undefined.
- Simplification: Rational expressions can often be simplified by factoring the numerator and denominator and canceling common factors. This is analogous to simplifying a numerical fraction, like reducing 6/8 to 3/4.
Multiplying Rational Expressions
Multiplying rational expressions follows a similar procedure to multiplying numerical fractions:
-
Factor Completely: Factor both the numerators and denominators of the expressions involved. This involves finding the prime factors of each polynomial. Techniques like factoring by grouping, difference of squares, and quadratic formula are frequently employed.
-
Multiply Numerators and Denominators: Multiply the numerators together to form a new numerator, and similarly, multiply the denominators together to form a new denominator.
-
Simplify: Cancel out any common factors that appear in both the numerator and the denominator. This simplification is crucial for obtaining the most concise form of the expression.
-
State Restrictions: It's vital to identify any restrictions on the variable before simplification, as canceling common factors might remove some restrictions from the simplified form. These restrictions are the values that would make any of the original denominators zero.
Example:
Multiply: (x² + 5x + 6) / (x² - 4) * (x - 2) / (x + 3)
-
Factor: (x + 2)(x + 3) / (x - 2)(x + 2) * (x - 2) / (x + 3)
-
Multiply: [(x + 2)(x + 3)(x - 2)] / [(x - 2)(x + 2)(x + 3)]
-
Simplify: 1 (after canceling common factors)
-
Restrictions: x ≠ 2, x ≠ -2, x ≠ -3
Dividing Rational Expressions
Dividing rational expressions is a slight variation on multiplication:
-
Invert and Multiply: Invert (or reciprocate) the second rational expression (the divisor) and change the division operation to multiplication.
-
Follow Multiplication Steps: Proceed with the steps for multiplying rational expressions: factor completely, multiply numerators and denominators, simplify, and state restrictions.
Example:
Divide: (x² + 5x + 6) / (x² - 4) ÷ (x + 3) / (x - 2)
-
Invert and Multiply: (x² + 5x + 6) / (x² - 4) * (x - 2) / (x + 3)
-
Follow Multiplication Steps (as shown in the previous example): The result is 1, with restrictions x ≠ 2, x ≠ -2, x ≠ -3.
The Importance of a Multiply and Divide Rational Expressions Calculator
Manual manipulation of rational expressions, especially those involving complex polynomials, is prone to errors. A calculator provides several key advantages:
-
Accuracy: Calculators minimize the risk of human errors in factoring, simplification, and identifying restrictions. They perform the calculations flawlessly, given correct input.
-
Efficiency: They significantly reduce the time and effort required for solving complex problems. This allows you to focus on understanding the concepts and applying them to more challenging problems.
-
Learning Tool: While calculators should not replace understanding the underlying principles, they can be used as a learning tool. By comparing your manual solution to the calculator's result, you can identify and correct errors in your work, strengthening your understanding.
-
Handling Complex Polynomials: Calculators excel at handling polynomials of higher degrees, which can be extremely challenging to factor manually.
Using a Multiply and Divide Rational Expressions Calculator: A Step-by-Step Guide
While the specific interface of online calculators varies, the general process is consistent. Here's a hypothetical step-by-step guide:
-
Input the Expressions: Enter the rational expressions accurately, ensuring correct use of parentheses and operators. Pay close attention to the placement of exponents and coefficients. Most calculators will use standard algebraic notation.
-
Specify the Operation: Clearly indicate whether you are multiplying or dividing the expressions.
-
Execute the Calculation: Press the "calculate" or equivalent button to initiate the computation.
-
Review the Result: The calculator will display the simplified result and may include a list of restrictions. Carefully check the output to ensure it makes sense in the context of the problem.
-
Verify Manually (If Necessary): For learning purposes, it's beneficial to verify the calculator's result by performing the manual calculations. This helps reinforce your understanding of the underlying mathematical principles.
Advanced Features and Considerations
Some advanced calculators may offer additional features:
-
Step-by-Step Solutions: Some calculators provide a detailed step-by-step breakdown of the solution process. This feature is invaluable for understanding the logic behind the simplification and for identifying where errors might have occurred in manual calculations.
-
Graphical Representation: Visualizing the expressions graphically can aid understanding. Advanced tools might show graphs of the functions represented by the rational expressions, enabling a deeper comprehension of their behavior.
-
Handling Complex Numbers: Some calculators can handle rational expressions involving complex numbers, extending the scope of problems that can be addressed.
Conclusion
Multiplying and dividing rational expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra. While understanding the underlying mathematical principles is crucial, leveraging a multiply and divide rational expressions calculator significantly enhances efficiency and accuracy. By using a calculator strategically as a learning tool and a problem-solving aid, you can master this skill with confidence and tackle increasingly complex problems. Remember to always check for restrictions and verify results to ensure a complete understanding of the process. The calculator is a powerful tool, but it’s your understanding of the underlying concepts that truly unlocks mathematical mastery.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
220 Pounds Is How Many Kilograms
Mar 25, 2025
-
Parallel Line And Perpendicular Line Calculator
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Much 145 Pounds Is In Kilograms
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is 160 Kg In Pounds
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Kilos Is 126 Pounds
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Multiply And Divide Rational Expressions Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
