Write The Following As An Exponential Expression
Greels
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
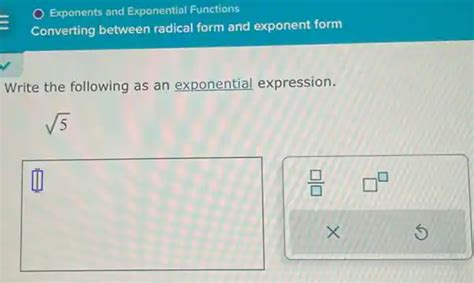
Table of Contents
Write the Following as an Exponential Expression: A Comprehensive Guide
Writing a number as an exponential expression involves expressing it as a base raised to a certain power (exponent). This seemingly simple concept forms the bedrock of many mathematical operations and is crucial in various fields, from scientific notation to complex calculations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of converting numbers into exponential expressions, exploring different scenarios and offering clear explanations to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Exponential Notation
Before diving into the conversion process, let's solidify our understanding of exponential notation. An exponential expression takes the form b<sup>n</sup>, where:
- b is the base: This is the number being multiplied repeatedly.
- n is the exponent: This indicates how many times the base is multiplied by itself. It's also known as the power or index.
For instance, 2<sup>3</sup> (read as "two to the power of three" or "two cubed") means 2 × 2 × 2 = 8. Here, 2 is the base, and 3 is the exponent.
Converting Numbers to Exponential Expressions: Basic Cases
The simplest cases involve converting numbers that are perfect powers of common bases (like 2, 3, 10, etc.). Let's explore these:
Example 1: Converting 64 to an Exponential Expression
64 can be expressed as repeated multiplication: 8 × 8 = 64. But we can go further. 8 itself is 2 × 2 × 2 = 2<sup>3</sup>. Therefore, 64 = 8 × 8 = (2<sup>3</sup>) × (2<sup>3</sup>) = 2<sup>6</sup>. So, the exponential expression for 64 is 2<sup>6</sup>.
Example 2: Converting 1000 to an Exponential Expression
1000 = 10 × 10 × 10 = 10<sup>3</sup>. This is a straightforward example where the base is 10 and the exponent is 3.
Example 3: Converting 81 to an Exponential Expression
81 can be expressed as 9 × 9 = 9<sup>2</sup>. However, we can also express it as 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 3<sup>4</sup>. This demonstrates that a number can often be written as an exponential expression with different bases. The key is to find the most simplified form.
Converting Numbers with Prime Factorization
For numbers that aren't immediately recognizable as perfect powers, prime factorization is invaluable. Prime factorization involves breaking a number down into its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
Example 4: Converting 72 to an Exponential Expression
- Find the prime factors: 72 = 2 × 36 = 2 × 2 × 18 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 9 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3.
- Rewrite using exponents: This gives us 2<sup>3</sup> × 3<sup>2</sup>.
Therefore, the exponential expression for 72 is 2<sup>3</sup> × 3<sup>2</sup>. Notice that we can't combine these because the bases are different.
Example 5: Converting 360 to an Exponential Expression
- Find the prime factors: 360 = 2 × 180 = 2 × 2 × 90 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 45 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 15 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5.
- Rewrite using exponents: This yields 2<sup>3</sup> × 3<sup>2</sup> × 5<sup>1</sup> (or simply 2<sup>3</sup> × 3<sup>2</sup> × 5).
Thus, the exponential expression for 360 is 2<sup>3</sup> × 3<sup>2</sup> × 5.
Dealing with Fractions and Decimals
Converting fractions and decimals to exponential expressions requires a slightly different approach.
Example 6: Converting 1/8 to an Exponential Expression
1/8 can be written as (1/2) × (1/2) × (1/2) = (1/2)<sup>3</sup>. Alternatively, since 8 = 2<sup>3</sup>, 1/8 = 1/2<sup>3</sup> = 2<sup>-3</sup>. This illustrates the use of negative exponents to represent reciprocals.
Example 7: Converting 0.00001 to an Exponential Expression
0.00001 can be written as 1/100000. Since 100000 = 10<sup>5</sup>, 0.00001 = 1/10<sup>5</sup> = 10<sup>-5</sup>. Again, a negative exponent is used to represent the decimal fraction.
Handling Larger Numbers and Scientific Notation
For very large or very small numbers, scientific notation is often used. This notation expresses a number as a value between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of 10.
Example 8: Converting 6,750,000,000 to an Exponential Expression
- Convert to scientific notation: 6.75 × 10<sup>9</sup>
- Express 6.75 as an exponential expression (if necessary): While 6.75 itself doesn't neatly simplify into a whole-number exponential expression, the scientific notation already provides a compact exponential form.
Thus, the exponential representation is 6.75 × 10<sup>9</sup>.
Example 9: Converting 0.00000000045 to an Exponential Expression
- Convert to scientific notation: 4.5 × 10<sup>-10</sup>
- Express 4.5 as an exponential expression (if necessary): Similar to the previous example, the scientific notation itself provides the most efficient exponential representation.
The exponential representation is 4.5 × 10<sup>-10</sup>.
Advanced Applications and Considerations
The concept of writing numbers as exponential expressions extends beyond basic numerical conversions. It's fundamental in:
- Simplifying algebraic expressions: Exponential rules allow for combining and simplifying terms involving exponents.
- Solving exponential equations: Understanding exponents is crucial for solving equations where the variable is in the exponent.
- Calculus and advanced mathematics: Exponents are ubiquitous in calculus, particularly in differentiation and integration.
- Computer science: Binary numbers (base 2) are extensively used in computer systems, relying heavily on exponential representation.
- Understanding compound interest and growth: Exponential functions are used to model exponential growth and decay in various contexts.
Troubleshooting Common Errors
- Incorrect base selection: Carefully choose the base that allows for the simplest exponential expression.
- Mistakes with negative exponents: Remember that a negative exponent represents a reciprocal.
- Errors in prime factorization: Ensure accurate prime factorization before converting to an exponential expression.
- Forgetting order of operations: When dealing with multiple exponents or operations, always follow the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS).
Conclusion
Converting numbers to exponential expressions is a fundamental skill in mathematics with far-reaching applications. Mastering this skill involves understanding the concept of bases and exponents, employing prime factorization for complex numbers, and utilizing scientific notation for very large or very small numbers. By practicing these techniques and addressing common pitfalls, you can confidently transform numerical representations into their efficient exponential forms. This proficiency will significantly improve your mathematical capabilities and deepen your understanding of various mathematical concepts and their real-world applications. Remember, consistent practice is key to mastering this important mathematical skill.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
91 Kg Is How Many Pounds
Mar 28, 2025
-
120 Km Is How Many Miles
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Miles In 250 Kilometers
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Kilograms In 175 Pounds
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Much Is 130 Lbs In Kg
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write The Following As An Exponential Expression . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
