What Is 95 Kilos In Pounds
Greels
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
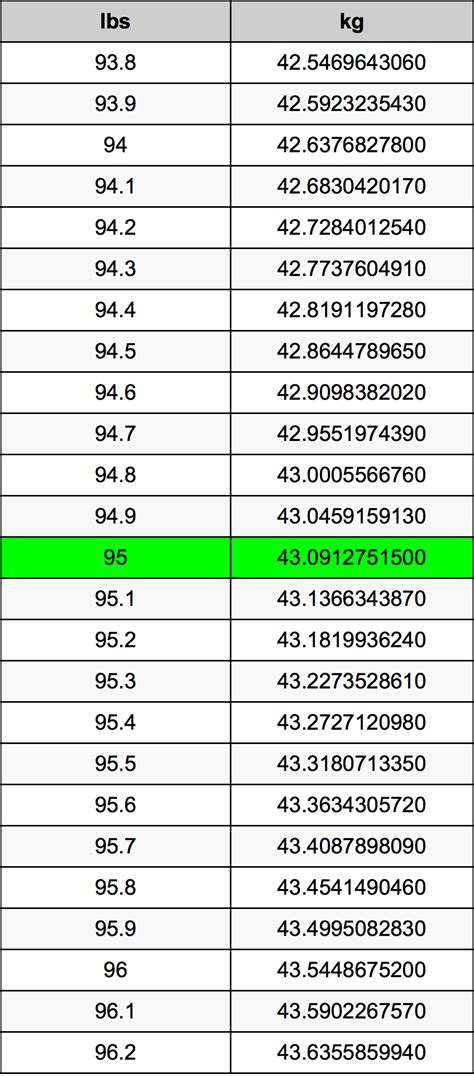
Table of Contents
What is 95 Kilos in Pounds? A Comprehensive Guide to Weight Conversions
The question, "What is 95 kilos in pounds?" might seem simple, but it opens a door to a broader understanding of weight measurement systems and their practical applications. This comprehensive guide will not only answer that question but also delve into the intricacies of metric and imperial systems, exploring their historical context, common uses, and the importance of accurate conversions.
Understanding Kilograms and Pounds: A Tale of Two Systems
Before we dive into the conversion, let's establish a foundational understanding of the two units involved: kilograms (kg) and pounds (lbs).
Kilograms (kg): This is the fundamental unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), often referred to as the metric system. Widely adopted globally, the kilogram is defined as being equal to the mass of the international prototype kilogram (IPK), a platinum-iridium cylinder kept under carefully controlled conditions near Paris. Its widespread use stems from the simplicity and logical structure of the metric system, where units are related by powers of ten.
Pounds (lbs): The pound is a unit of mass in the imperial system of units, predominantly used in the United States and a few other countries. Historically derived from various standards, the modern pound is defined in relation to the kilogram. The imperial system, unlike the metric system, is less coherent, lacking a consistent system of prefixes and relationships between units.
The Conversion: 95 Kilograms to Pounds
The conversion factor between kilograms and pounds is approximately 2.20462. Therefore, to convert 95 kilograms to pounds, we simply multiply:
95 kg * 2.20462 lbs/kg ≈ 209.44 lbs
Therefore, 95 kilograms is approximately 209.44 pounds. This is a crucial conversion for anyone dealing with international trade, shipping, or any situation requiring the precise interchange of weight measurements between metric and imperial systems.
Beyond the Conversion: Practical Applications and Importance
Accurate weight conversions extend far beyond simple mathematical exercises. They are essential in numerous fields, including:
-
International Trade: Ensuring consistent weight measurements is vital for fair trade practices, preventing misunderstandings and disputes between countries using different systems. Inaccurate conversions can lead to financial losses and contractual disagreements.
-
Shipping and Logistics: Accurate weight is paramount for calculating shipping costs, ensuring proper load distribution in vehicles, and complying with regulations related to weight limits on roads and airways.
-
Healthcare and Medicine: Dosage calculations in pharmaceuticals, as well as monitoring patient weight for health assessments, necessitates accurate conversions between metric and imperial units to ensure patient safety.
-
Food Industry: Food packaging often involves both metric and imperial units, demanding precision in weight measurement during production, packaging, and labeling to comply with regulations and meet customer expectations.
-
Engineering and Construction: Precise weight calculations are critical in engineering and construction projects for structural integrity, load-bearing capacity, and material selection.
-
Scientific Research: Weight conversions are routinely used in scientific experiments and data analysis, ensuring accurate recording and interpretation of research findings.
Mastering Weight Conversions: Tips and Tools
While simple calculations like the one above are straightforward, mastering weight conversions requires a nuanced understanding of the different units and their interrelationships. Here are some practical tips and tools:
-
Online Converters: Numerous online calculators provide instant conversions between kilograms and pounds and other units of weight and measurement. These tools are helpful for quick conversions and verification. However, it's crucial to rely on reputable websites known for accuracy.
-
Understanding Significant Figures: In scientific and engineering applications, paying close attention to significant figures is essential for maintaining accuracy. The number of significant figures in the result should reflect the precision of the input values.
-
Approximations vs. Precision: While quick approximations are acceptable in some situations, for critical applications, precise conversions are crucial. Knowing when to use an approximation and when to require higher precision depends on the context.
-
Unit Consistency: Maintaining consistent units throughout calculations is essential to avoid errors. Avoid mixing metric and imperial units within the same calculation unless using explicit conversion factors.
Exploring the Historical Context: Evolution of Weight Measurement
The systems we use today, both metric and imperial, are products of centuries of evolution, reflecting different cultural and technological influences. Understanding this historical context enriches our appreciation of the current systems and the complexities of measurement.
-
Ancient Systems: Ancient civilizations had diverse systems of weights and measures, often based on readily available objects like grains of barley or specific body parts. These systems lacked standardization and varied significantly across regions.
-
The Development of the Metric System: The metric system emerged in the late 18th century as a response to the need for a more rational and coherent system of measurement. Its decimal-based structure simplified calculations and promoted standardization across scientific and commercial activities.
-
The Persistence of the Imperial System: The imperial system, with its origins in various historical standards, persisted in several countries, particularly the United States. While efforts have been made to transition to the metric system, the imperial system remains deeply entrenched in some sectors.
Beyond Kilograms and Pounds: Other Units of Weight
It is also important to understand that kilograms and pounds are not the only units used to measure weight. Other units exist, with their own specific contexts and applications:
-
Grams (g): A smaller unit within the metric system, commonly used for measuring smaller quantities of substances.
-
Ounces (oz): A smaller unit within the imperial system, frequently used for measuring smaller quantities of goods.
-
Tons (t): Both metric tons (1000 kg) and imperial tons (2000 lbs) are used to measure very large weights.
-
Stone: A less common unit, primarily used in the United Kingdom, equivalent to 14 pounds.
Understanding the relationship between these units is crucial for effective communication and accurate calculations across different contexts.
Conclusion: The Importance of Accuracy and Understanding
The seemingly simple question of converting 95 kilograms to pounds highlights the importance of understanding different weight measurement systems and their appropriate application. Accurate conversions are crucial for various fields, from international trade to healthcare. Mastering these conversions not only ensures accuracy in practical applications but also provides a deeper understanding of the evolution of measurement systems and their significance in the world. This understanding allows for greater precision, clearer communication, and ultimately, safer and more efficient practices across numerous industries and disciplines. Remember to always double-check your conversions, especially in situations where precision is paramount.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
200 Is 10 Percent Of What
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Grams In 11 Ounces
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 68 Cm
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Meters Is 18 Feet
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 76 Kg In Lbs
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 95 Kilos In Pounds . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
