Slopes Of Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Calculator
Greels
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
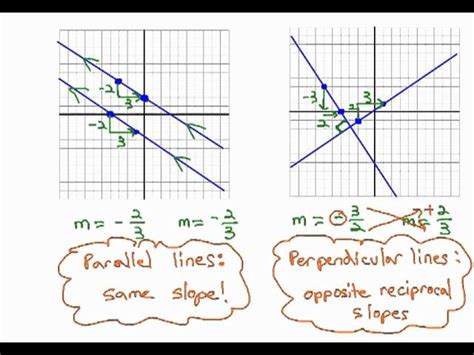
Table of Contents
Slopes of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the relationship between the slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines is fundamental in geometry and various applications within mathematics, physics, and engineering. This comprehensive guide will delve into the concept of slopes, explain how to calculate them, and demonstrate how to use a slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines calculator effectively. We'll also cover practical applications and explore related geometrical concepts.
What is Slope?
The slope of a line is a measure of its steepness or inclination. It represents the rate of change of the y-coordinate with respect to the x-coordinate. A higher slope indicates a steeper line, while a slope of zero signifies a horizontal line. A vertical line has an undefined slope. The slope is often represented by the letter 'm'.
Formulas for calculating slope:
- Given two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2): m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
- Given the equation of a line in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b): m = the coefficient of x.
Interpreting Slope Values:
- Positive Slope (m > 0): The line rises from left to right.
- Negative Slope (m < 0): The line falls from left to right.
- Zero Slope (m = 0): The line is horizontal.
- Undefined Slope: The line is vertical.
Parallel Lines and Their Slopes
Parallel lines are lines that never intersect. A key characteristic of parallel lines is that they have the same slope. This is true regardless of their y-intercepts (the point where the line crosses the y-axis).
Example:
Let's say we have two lines:
- Line 1: y = 2x + 3
- Line 2: y = 2x - 5
Both lines have a slope (m) of 2. Therefore, they are parallel.
Perpendicular Lines and Their Slopes
Perpendicular lines intersect at a right angle (90 degrees). The relationship between their slopes is more complex. If two lines are perpendicular, the product of their slopes is -1. In other words, the slope of one line is the negative reciprocal of the slope of the other line.
Formula: m1 * m2 = -1 where m1 and m2 are the slopes of the perpendicular lines.
Example:
Let's say we have two lines:
- Line 1: y = 3x + 2 (m1 = 3)
- Line 2: y = (-1/3)x + 7 (m2 = -1/3)
The product of their slopes is: 3 * (-1/3) = -1. Therefore, these lines are perpendicular.
Using a Slopes of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Calculator
A slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines calculator is a valuable tool for quickly and accurately determining whether two lines are parallel or perpendicular. These calculators typically require you to input the coordinates of two points for each line or the equations of the lines themselves. The calculator then computes the slopes and determines the relationship between the lines.
Steps to use a typical calculator:
-
Input the coordinates: Enter the x and y coordinates of two points for each line. Or, input the equations of the lines in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) or standard form (Ax + By = C).
-
Calculate the slopes: The calculator will automatically compute the slope of each line using the formula m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) or by extracting the slope from the equation of the line.
-
Determine the relationship: The calculator will analyze the slopes and indicate whether the lines are parallel (same slope), perpendicular (product of slopes is -1), or neither.
-
Analyze the Results: Understand the output. The calculator should clearly state whether the lines are parallel, perpendicular, or neither, providing the calculated slopes for each line.
Practical Applications
The concept of parallel and perpendicular lines, and their slopes, finds extensive use across various fields:
-
Civil Engineering: Designing roads, bridges, and buildings often requires ensuring that structural components are parallel or perpendicular for stability and functionality.
-
Computer Graphics: Creating 2D and 3D graphics relies heavily on manipulating lines and shapes, where understanding parallel and perpendicular lines is crucial for accurate representations and transformations.
-
Physics: Analyzing motion, forces, and vectors often involves working with lines and their slopes, especially when dealing with concepts like velocity and acceleration.
-
Cartography: Mapmaking utilizes concepts of parallel and perpendicular lines to represent geographical features accurately and create effective map projections.
-
Architecture: Determining the structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of a building design often relies on the precise relationship between parallel and perpendicular lines.
Advanced Concepts and Considerations
-
Lines in 3D Space: Extending the concept of slopes to three-dimensional space requires understanding vectors and their components. Parallel and perpendicular lines in 3D are defined by the relationships between their direction vectors.
-
Non-linear Relationships: While this guide focuses on linear equations and their slopes, the concept of slopes can be extended to tangent lines in calculus, which deal with the instantaneous rate of change of a non-linear function.
-
Error Handling: When using calculators or manually calculating slopes, be mindful of potential errors. Dividing by zero, for example, is undefined and represents a vertical line. Always double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion
Understanding slopes and their application in determining the relationships between parallel and perpendicular lines is crucial in various fields. By mastering these concepts and effectively utilizing a slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines calculator, you can enhance your problem-solving skills in mathematics, geometry, and beyond. Remember to practice consistently and explore different examples to build a solid understanding of this important geometric principle. Using a calculator can be a great tool for speed and accuracy, but understanding the underlying mathematics is key to fully grasping the concepts. This allows for critical thinking and problem-solving, even when a calculator isn't available.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
4 Foot 9 Is How Many Inches
Mar 25, 2025
-
Square Root Of X 2 X 4
Mar 25, 2025
-
28 Grams Is How Many Ounces
Mar 25, 2025
-
System Of Linear Equations Calculator Matrix
Mar 25, 2025
-
Cross Product Of 3 Vectors Calculator
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Slopes Of Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
