Separation Of Variables Differential Equations Calculator
Greels
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
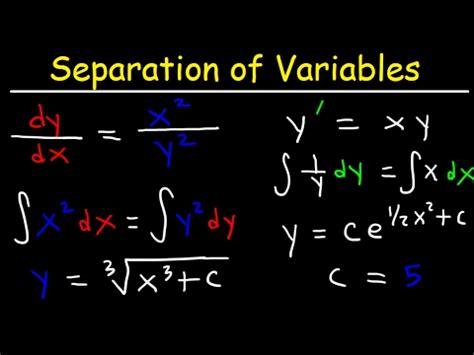
Table of Contents
Separation of Variables Differential Equations Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Solving differential equations is a cornerstone of many scientific and engineering disciplines. While some equations yield to straightforward analytical solutions, many require more sophisticated techniques. One such powerful method is the separation of variables, a technique particularly useful for solving ordinary differential equations (ODEs) of a specific form. This article will explore the separation of variables method, its limitations, and how to effectively utilize calculators – both online and offline – to assist in the process. We will also delve into the nuances of handling different types of equations and the importance of verifying solutions.
Understanding Separation of Variables
The separation of variables method is applicable to first-order ordinary differential equations that can be expressed in the form:
dy/dx = f(x)g(y)
where f(x) is a function solely of x, and g(y) is a function solely of y. The core idea is to "separate" the variables x and y, placing all terms involving x on one side of the equation and all terms involving y on the other. This allows for integration on both sides, leading to the general solution.
Steps Involved:
-
Separate the Variables: Rewrite the equation so that all terms containing 'y' (including dy) are on one side, and all terms containing 'x' (including dx) are on the other. This usually involves algebraic manipulation.
-
Integrate Both Sides: Integrate both sides of the separated equation with respect to their respective variables. Remember to include the constant of integration (+C). This constant is crucial for representing the family of solutions.
-
Solve for y: If possible, explicitly solve the resulting equation for y as a function of x. This may involve algebraic manipulation or the use of inverse functions.
-
Apply Initial Conditions (if given): If an initial condition (e.g., y(0) = 1) is provided, substitute the values into the general solution to determine the specific constant of integration 'C' and obtain the particular solution.
Example: Illustrating the Process
Let's solve the differential equation:
dy/dx = x/y
-
Separate Variables:
y dy = x dx
-
Integrate:
∫y dy = ∫x dx
y²/2 = x²/2 + C (where C is the constant of integration)
-
Solve for y:
y² = x² + 2C
y = ±√(x² + 2C)
This gives us the general solution. To find a particular solution, we'd need an initial condition.
Limitations of Separation of Variables
It's crucial to understand that the separation of variables method is not a universal solution for all ODEs. It's only applicable to equations that can be written in the specific separable form described earlier. Equations involving terms like x*y or more complex functions of both x and y are generally not solvable using this method. In such cases, other techniques like integrating factors or numerical methods become necessary.
Utilizing Calculators for Assistance
While understanding the underlying mathematical principles is paramount, calculators can significantly streamline the process, especially for complex integrations or algebraic manipulations.
Online Separation of Variables Calculators
Many websites offer free online calculators specifically designed to solve differential equations using the separation of variables technique. These tools usually require inputting the equation in a specific format, after which they perform the separation, integration, and solve for y, presenting the general and, if possible, particular solution. Remember to always cross-check the calculator's output with your own manual calculations to ensure accuracy.
Offline Mathematical Software
Advanced mathematical software packages like Mathematica, Maple, or MATLAB offer powerful symbolic computation capabilities. These platforms can handle complex differential equations, including those solvable by separation of variables, and provide detailed step-by-step solutions. They are particularly beneficial for dealing with intricate integrations or when exploring more advanced aspects of differential equation solutions.
Handling Different Types of Equations
The separation of variables method, while seemingly straightforward, can present variations depending on the specific form of the differential equation. Here are some common scenarios:
Equations with Exponential Functions:
Equations involving exponential functions often require careful handling of the integration steps. For instance, consider:
dy/dx = e<sup>x</sup>e<sup>y</sup>
This requires understanding the properties of exponential functions to separate and integrate correctly.
Equations with Trigonometric Functions:
Similarly, equations involving trigonometric functions necessitate familiarity with trigonometric identities and integration techniques.
Equations with Homogeneous Functions:
Some ODEs can be transformed into a separable form through substitution. Homogeneous equations, where the function is homogeneous of degree zero, are good candidates for this transformation. This involves substituting y = vx, where 'v' is a new function.
Verifying Solutions
It's essential to verify any solution obtained, whether through manual calculation or using a calculator. Substitute the solution back into the original differential equation to ensure it satisfies the equation. This step helps to identify potential errors in calculation or misuse of the technique. This verification is especially critical when dealing with more complex equations or when using automated calculators.
Advanced Applications and Extensions
While this guide focuses on the fundamental aspects of the separation of variables method, its applications extend far beyond basic examples. In advanced calculus and engineering fields, we encounter partial differential equations that are also amenable to separation of variables. This involves extending the technique to multiple variables and employing techniques like Fourier series for solving complex boundary value problems. However, these advanced topics often necessitate a deeper understanding of calculus and related mathematical concepts.
Conclusion: Mastering Separation of Variables
The separation of variables method provides a powerful and efficient approach for solving a specific class of ordinary differential equations. While calculators can assist in the computational aspects, a solid understanding of the underlying mathematical principles is crucial for effectively employing this method and interpreting its results. This understanding encompasses the ability to recognize separable equations, perform accurate integrations, handle various function types, and critically verify obtained solutions. By combining a strong theoretical foundation with the strategic use of computational tools, one can effectively solve a wide range of differential equations using the separation of variables technique and contribute effectively to diverse fields where these techniques are essential. Remember to always verify your solutions and consult additional resources for in-depth exploration of this vital mathematical tool.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 15 Percent Of 45
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 35 M
Mar 28, 2025
-
Parallel Lines Cut By A Transversal Calculator
Mar 28, 2025
-
45 Kg Is How Many Pounds
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 8000 Meters
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Separation Of Variables Differential Equations Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
