Rectangular Equation To Polar Form Calculator
Greels
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
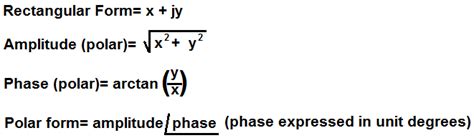
Table of Contents
Rectangular Equation to Polar Form Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting rectangular equations to polar form is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in calculus and analytic geometry. While the process is straightforward, it can become tedious, especially with complex equations. This is where a rectangular equation to polar form calculator proves invaluable. This article will delve into the intricacies of this conversion, explaining the underlying principles, providing step-by-step examples, and highlighting the advantages of using a calculator to streamline the process. We'll also explore various applications and common pitfalls to watch out for.
Understanding Rectangular and Polar Coordinate Systems
Before diving into the conversion process, it's crucial to understand the two coordinate systems involved.
Rectangular Coordinates (Cartesian Coordinates): This system uses two perpendicular axes, the x-axis and the y-axis, to locate a point in a plane using its horizontal (x) and vertical (y) distances from the origin (0,0). A point is represented as an ordered pair (x, y).
Polar Coordinates: This system uses a distance (r) from the origin and an angle (θ) measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis to locate a point. A point is represented as an ordered pair (r, θ).
The relationship between these two systems is fundamental to the conversion process.
The Conversion Formulas: The Heart of the Transformation
The core of converting a rectangular equation to polar form lies in the following conversion formulas:
- x = r cos θ
- y = r sin θ
- r² = x² + y²
- tan θ = y/x (Note: This formula has limitations, discussed later)
These formulas provide the mathematical bridge between the rectangular (x, y) and polar (r, θ) representations of a point. By substituting these formulas into a rectangular equation, you transform it into a polar equation.
Step-by-Step Conversion Process: A Practical Approach
Let's illustrate the conversion process with a few examples, showcasing the step-by-step method.
Example 1: Converting a Simple Linear Equation
Let's convert the rectangular equation x + y = 1 to polar form.
-
Substitute: Replace 'x' with 'r cos θ' and 'y' with 'r sin θ'. This gives us: r cos θ + r sin θ = 1
-
Solve for r: Factor out 'r': r(cos θ + sin θ) = 1
-
Isolate r: Divide both sides by (cos θ + sin θ): r = 1 / (cos θ + sin θ)
Therefore, the polar form of the equation x + y = 1 is r = 1 / (cos θ + sin θ).
Example 2: Converting a Circle Equation
Let's convert the rectangular equation x² + y² = 4 (a circle with radius 2 centered at the origin) to polar form.
-
Substitute: Recall that r² = x² + y². Substitute this directly into the equation: r² = 4
-
Solve for r: Take the square root of both sides: r = ±2
Therefore, the polar form of the equation x² + y² = 4 is r = 2 (we usually consider only the positive solution for the radius).
Example 3: Converting a More Complex Equation
Let's tackle a slightly more challenging equation: x² - y² = 1.
-
Substitute: Replace 'x' and 'y' with their polar equivalents: (r cos θ)² - (r sin θ)² = 1
-
Simplify: Expand and simplify the equation: r²(cos²θ - sin²θ) = 1
-
Solve for r: Divide both sides by (cos²θ - sin²θ): r² = 1 / (cos²θ - sin²θ)
-
Further Simplification (Optional): Using trigonometric identities, we can simplify this further. Recall that cos(2θ) = cos²θ - sin²θ. Thus, the equation becomes: r² = 1 / cos(2θ) or r² = sec(2θ)
Therefore, the polar form of the equation x² - y² = 1 is r² = sec(2θ) or r = ±√(sec(2θ)).
Utilizing a Rectangular Equation to Polar Form Calculator
While manual conversion is educational, it can be time-consuming and prone to errors, especially with complex equations. This is where a rectangular equation to polar form calculator becomes invaluable. These calculators typically require you to input the rectangular equation, and they will instantly output the equivalent polar form. They handle the algebraic manipulations and simplifications automatically, saving you significant time and effort.
Advantages of Using a Calculator
- Speed and Efficiency: Calculators perform the conversions much faster than manual calculations.
- Accuracy: They minimize the risk of algebraic errors, ensuring accurate results.
- Handling Complex Equations: They effortlessly handle complex equations that would be tedious to solve manually.
- Educational Tool: While not a replacement for understanding the underlying principles, a calculator can be a valuable educational tool by allowing you to check your work and explore various examples quickly.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
- Domain Restrictions: Be mindful of any domain restrictions on the original rectangular equation. These restrictions will translate to the polar form.
- The Tangent Function: Remember that the formula tan θ = y/x has limitations. It doesn't provide information about the quadrant in which the point lies, so careful consideration is needed for equations where the origin is not included.
- Multiple Solutions: Some equations may have multiple polar representations. A calculator may provide one solution, but other valid representations might exist.
- Understanding the Output: Always check the output of the calculator to ensure it makes sense within the context of the original equation.
Applications of Polar Coordinates and Conversions
Polar coordinates find extensive applications across various fields:
- Physics: Describing motion in circular paths, analyzing rotational dynamics.
- Engineering: Designing circular structures, analyzing electrical circuits (phasors).
- Computer Graphics: Creating curves and shapes, defining transformations.
- Navigation: Representing geographical positions (latitude and longitude).
- Astronomy: Modeling planetary orbits.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Conversions
Beyond simple equations, the principles of conversion can be extended to handle more complex scenarios involving:
- Parametric Equations: Converting parametric equations defined in rectangular coordinates to polar form.
- Implicit Equations: Converting implicit equations (where x and y are not explicitly solved for) into polar form.
- Equations with Multiple Variables: Extending the concepts to higher dimensions.
Conclusion: Mastering the Conversion
Converting rectangular equations to polar form is a crucial skill in mathematics and its applications. While understanding the underlying principles and the conversion formulas is essential, utilizing a rectangular equation to polar form calculator significantly streamlines the process, making it efficient and accurate. By combining manual understanding with the power of computational tools, you can effectively master this fundamental transformation and confidently apply it to various mathematical and real-world problems. Remember to always critically evaluate the results and consider potential domain restrictions and multiple solutions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Find The Radius Of Convergence Calculator
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Tall Is 65inches In Feet
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Much Is 62 Inches In Feet
Mar 28, 2025
-
161 Cm To Inch And Feet
Mar 28, 2025
-
100 99 100 99 100 100
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Rectangular Equation To Polar Form Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
