Radius Of Convergence Power Series Calculator
Greels
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
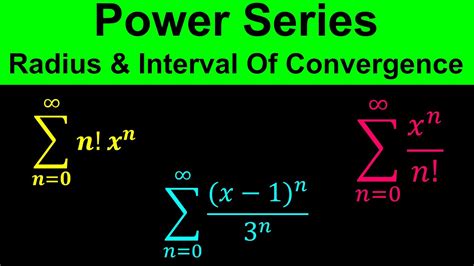
Table of Contents
Radius of Convergence Power Series Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the radius of convergence of a power series can be a tedious and error-prone process. Manually calculating it often involves intricate steps and a deep understanding of concepts like the ratio test, root test, and Cauchy-Hadamard theorem. This is where a radius of convergence power series calculator becomes invaluable. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, utilizing, and interpreting the results from such calculators, alongside a thorough exploration of the underlying mathematical principles.
Understanding Power Series and Radius of Convergence
A power series is an infinite series of the form:
∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> a<sub>n</sub>(x - c)<sup>n</sup>
where:
- a<sub>n</sub> represents the coefficients of the series.
- x is the variable.
- c is the center of the series (often 0).
The radius of convergence, denoted by R, defines the interval around the center c where the power series converges. Within this interval, the series produces a finite sum. Outside this interval (|x - c| > R), the series diverges, meaning it doesn't approach a finite limit. At the endpoints of the interval (|x - c| = R), the convergence needs to be tested separately; it may converge at one endpoint, both endpoints, or neither.
Methods for Determining Radius of Convergence
Several methods exist to determine the radius of convergence, each with its strengths and weaknesses:
1. The Ratio Test
The ratio test is a frequently used method. It involves calculating the limit:
L = lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |a<sub>n+1</sub>(x - c)<sup>n+1</sup> / a<sub>n</sub>(x - c)<sup>n</sup>| = lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |a<sub>n+1</sub> / a<sub>n</sub>| |x - c|
If L < 1, the series converges. If L > 1, the series diverges. If L = 1, the test is inconclusive, and other methods must be used. The radius of convergence is given by 1/lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |a<sub>n+1</sub> / a<sub>n</sub>|
2. The Root Test
The root test provides an alternative approach:
L = lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |a<sub>n</sub>(x - c)<sup>n</sup>|<sup>1/n</sup> = lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |a<sub>n</sub>|<sup>1/n</sup> |x - c|
Similar to the ratio test, if L < 1, the series converges; if L > 1, it diverges. If L = 1, the test is inconclusive. The radius of convergence is given by 1/lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |a<sub>n</sub>|<sup>1/n</sup>
3. The Cauchy-Hadamard Theorem
This theorem provides a more general approach, especially useful for complex power series:
1/R = lim sup<sub>n→∞</sub> |a<sub>n</sub>|<sup>1/n</sup>
The lim sup (limit superior) is the supremum (least upper bound) of the set of subsequential limits.
Limitations of Manual Calculation
Manually applying these methods can be challenging, especially for complex power series or when dealing with intricate coefficient patterns. Errors in calculation are easily introduced, potentially leading to inaccurate results. This highlights the need for a reliable radius of convergence power series calculator.
The Advantages of Using a Radius of Convergence Power Series Calculator
A well-designed calculator offers significant advantages:
- Accuracy: Eliminates human calculation errors, providing reliable and precise results.
- Efficiency: Saves significant time and effort compared to manual calculations.
- Ease of Use: Simplifies the process, making it accessible even to users with limited mathematical experience.
- Handling Complexity: Can easily handle power series with complex coefficient expressions that would be extremely difficult to solve manually.
- Immediate Feedback: Provides instantaneous results, enabling rapid iteration and experimentation.
How to Use a Radius of Convergence Power Series Calculator (General Steps)
While the specific interface varies among different calculators, the general steps usually involve:
-
Inputting the Power Series: Enter the coefficients (a<sub>n</sub>) of the power series. Many calculators allow various input formats, including explicit formulas for a<sub>n</sub> if a pattern exists, or a sequence of coefficients.
-
Specifying the Center: Identify and input the center c of the power series.
-
Selecting the Method: Some calculators may offer options to choose between the ratio test, root test, or other methods. If not specified, the calculator will likely utilize an appropriate algorithm.
-
Running the Calculation: Initiate the calculation process.
-
Interpreting the Results: The calculator will typically output the radius of convergence R. You might also get information on the interval of convergence, including an indication of convergence at the endpoints.
Interpreting the Results and the Interval of Convergence
The radius of convergence R provides the distance from the center c where the series converges. The interval of convergence is then given by:
(c - R, c + R)
However, remember to separately check the convergence at the endpoints (c - R) and (c + R) by substituting these values into the original power series and applying convergence tests like the alternating series test or other relevant tests.
Advanced Features in Some Calculators
Some advanced radius of convergence power series calculators might include:
- Graphical Representation: Visualizing the convergence/divergence of the series.
- Step-by-Step Solutions: Showing the detailed calculation steps, which can be beneficial for educational purposes.
- Support for Different Types of Series: Handling various types of series beyond the basic power series form.
- Complex Number Support: Accommodating complex coefficients and variables.
Examples of Power Series and Their Radii of Convergence
Let's consider a few examples to illustrate the concepts:
Example 1: ∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> x<sup>n</sup> (Geometric Series)
This is a simple geometric series with a<sub>n</sub> = 1 and c = 0. Using the ratio test:
L = lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |(x<sup>n+1</sup>) / (x<sup>n</sup>)| = |x|
The series converges if |x| < 1, thus R = 1. The interval of convergence is (-1, 1). At x = 1, it diverges; at x = -1, it converges to 1/2.
Example 2: ∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> (x - 2)<sup>n</sup> / n!
Here, a<sub>n</sub> = 1/n! and c = 2. Applying the ratio test:
L = lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |[(x - 2)<sup>n+1</sup> / (n + 1)!] / [(x - 2)<sup>n</sup> / n!]| = lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |(x - 2) / (n + 1)| = 0
Since L = 0 < 1 for all x, the radius of convergence is infinite (R = ∞). The series converges for all x.
Example 3: ∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> n! x<sup>n</sup>
Here, a<sub>n</sub> = n! and c = 0. Applying the ratio test:
L = lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |[(n + 1)! x<sup>n+1</sup>] / [n! x<sup>n</sup>]| = lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |(n + 1)x|
L < 1 only if x = 0. Therefore, R = 0. The series only converges at x = 0.
Conclusion
Calculating the radius of convergence of a power series is crucial for understanding the behavior and applicability of the series. While manual calculations are possible, they are often time-consuming and prone to errors. A radius of convergence power series calculator offers a highly efficient and accurate alternative, simplifying the process and making it more accessible to a wider range of users. By understanding the underlying mathematical principles and effectively using such calculators, you can confidently analyze power series and gain valuable insights into their convergence properties. Remember to always check endpoint convergence separately to fully define the interval of convergence. The availability of online calculators equipped with various functionalities makes the task of determining the radius and interval of convergence significantly easier and more reliable.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Pounds Is 73 Kg
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Much Is 62 Kg In Pounds
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is 60 Pounds
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 105 Days From Today
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Pounds Are In 48 Ounces
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Radius Of Convergence Power Series Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
