Power Series Interval Of Convergence Calculator
Greels
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
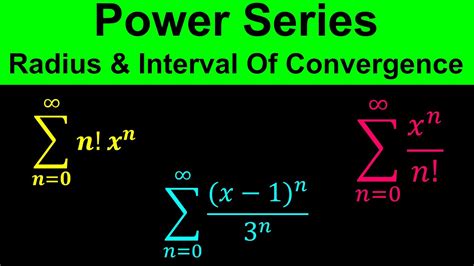
Table of Contents
Power Series Interval of Convergence Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
The world of mathematics, especially calculus, often involves complex computations. One such area is determining the interval of convergence for power series. Manually calculating this can be time-consuming and prone to errors. This is where a power series interval of convergence calculator becomes invaluable. This comprehensive guide explores the concept of power series, their intervals of convergence, and how to effectively use calculators to determine them. We'll also delve into the underlying mathematical principles and provide practical examples.
Understanding Power Series
A power series is an infinite series of the form:
∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> a<sub>n</sub>(x - c)<sup>n</sup> = a<sub>0</sub> + a<sub>1</sub>(x - c) + a<sub>2</sub>(x - c)² + a<sub>3</sub>(x - c)³ + ...
where:
- a<sub>n</sub> are the coefficients of the series (constants).
- x is a variable.
- c is the center of the power series (a constant).
Power series are fundamental in calculus because they allow us to represent many functions as infinite sums. This representation can simplify complex calculations and provide insights into the behavior of functions. Examples of functions commonly represented by power series include:
- Exponential function: e<sup>x</sup> = ∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> x<sup>n</sup>/n!
- Trigonometric functions: sin(x) = ∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> (-1)<sup>n</sup>x<sup>2n+1</sup>/(2n+1)! and cos(x) = ∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> (-1)<sup>n</sup>x<sup>2n</sup>/(2n)!
- Geometric series: 1/(1-x) = ∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> x<sup>n</sup> (for |x| < 1)
The Interval of Convergence
The crucial aspect of a power series is its interval of convergence. This is the range of x-values for which the series converges to a finite sum. Outside this interval, the series diverges (either to infinity or oscillates without settling on a value). The interval of convergence is often expressed as an open or closed interval: (a, b), [a, b], (a, b], or [a, b). The endpoints a and b need to be checked separately to determine whether the series converges at those points.
Determining the Interval of Convergence
The primary method for finding the interval of convergence involves the ratio test or the root test.
1. Ratio Test:
The ratio test states that if lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |a<sub>n+1</sub>(x - c) / a<sub>n</sub>| = L, then:
- If L < 1, the series converges absolutely.
- If L > 1, the series diverges.
- If L = 1, the test is inconclusive, and other methods must be used.
2. Root Test:
The root test is an alternative that considers the limit:
lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |a<sub>n</sub>(x - c)|<sup>1/n</sup> = L
The convergence criteria are the same as the ratio test. Sometimes, the root test is easier to apply than the ratio test, especially when dealing with series involving factorials or nth roots.
Applying the Tests and Checking Endpoints:
- Apply the ratio or root test: Determine the limit L in terms of x.
- Find the radius of convergence: The radius of convergence, R, is the distance from the center 'c' to the endpoints of the interval of convergence. It's determined by solving the inequality |L| < 1 for x. The solution will usually be of the form |x - c| < R.
- Determine the interval: The interval is then (c - R, c + R).
- Check endpoints: Substitute x = c - R and x = c + R into the original power series. Use other convergence tests (like the comparison test, integral test, alternating series test) to determine if the series converges at each endpoint. This determines whether the endpoints are included in the interval (resulting in closed brackets) or excluded (resulting in open brackets).
Power Series Interval of Convergence Calculator: Functionality and Usage
A power series interval of convergence calculator automates these steps. These calculators typically require the user to input:
- The coefficients a<sub>n</sub>: This can be input as a general formula (e.g., a<sub>n</sub> = 1/n!) or as a sequence of coefficients. The calculator must have robust pattern recognition to handle various forms of coefficient expressions.
- The center c: The point around which the power series is expanded.
- The preferred test: Some calculators offer the option to choose between the ratio test and the root test.
Output: The calculator will then output:
- The radius of convergence R: The distance from the center to the endpoints.
- The interval of convergence: The range of x-values for which the power series converges, including the appropriate brackets (open or closed) at the endpoints. The calculator should clearly indicate whether the series converges at each endpoint.
- Steps (optional): Some advanced calculators provide a detailed step-by-step solution, demonstrating the application of the chosen convergence test and the endpoint checks, which is crucial for educational purposes.
Choosing a Calculator
When choosing a power series interval of convergence calculator, consider these factors:
- Accuracy: The calculator should produce precise results.
- Ease of use: The interface should be intuitive and user-friendly.
- Step-by-step solution (optional): This feature is beneficial for learning and understanding the process.
- Support for different coefficient formats: The calculator should handle various ways of expressing coefficients.
- Handling of edge cases: The calculator should correctly handle series with unusual convergence properties.
Practical Examples
Let's illustrate the process with a couple of examples:
Example 1:
Consider the power series: ∑<sub>n=1</sub><sup>∞</sup> (x - 2)<sup>n</sup>/n
-
Ratio test: lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |((x - 2)<sup>n+1</sup>/(n+1)) / ((x - 2)<sup>n</sup>/n)| = lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |(x - 2)n/(n+1)| = |x - 2|
-
Radius of convergence: |x - 2| < 1, so R = 1.
-
Interval: (1, 3)
-
Endpoints:
- x = 1: ∑<sub>n=1</sub><sup>∞</sup> (-1)<sup>n</sup>/n (converges by the alternating series test).
- x = 3: ∑<sub>n=1</sub><sup>∞</sup> 1/n (diverges – harmonic series).
-
Final Interval of Convergence: [1, 3)
Example 2:
Consider the power series: ∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> (2x)<sup>n</sup>
-
Ratio test: lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |(2x)<sup>n+1</sup> / (2x)<sup>n</sup>| = |2x|
-
Radius of convergence: |2x| < 1 => |x| < 1/2, so R = 1/2.
-
Interval: (-1/2, 1/2)
-
Endpoints:
- x = -1/2: ∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> (-1)<sup>n</sup> (diverges).
- x = 1/2: ∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> 1 (diverges).
-
Final Interval of Convergence: (-1/2, 1/2)
These examples demonstrate the importance of checking the endpoints, as the convergence behavior at these points can vary.
Conclusion
Determining the interval of convergence for power series is a crucial aspect of understanding and working with these fundamental mathematical objects. While manual calculation is possible, it is often complex and error-prone. A power series interval of convergence calculator provides a convenient and efficient way to determine this critical information. By understanding the underlying mathematical principles and utilizing the capabilities of a well-designed calculator, you can confidently analyze and work with power series in your mathematical endeavors. Remember to choose a calculator that offers accuracy, ease of use, and potentially step-by-step solutions for educational purposes. This will significantly enhance your understanding and efficiency in handling power series and their convergence properties.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Pounds Is 81 Kilograms
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 53 Mm
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Much Is 26 Kg In Pounds
Mar 28, 2025
-
89 Kilograms Is How Many Pounds
Mar 28, 2025
-
7 5 Kg Is How Many Pounds
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Power Series Interval Of Convergence Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
