Polynomial Long Division Calculator With Steps
Greels
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
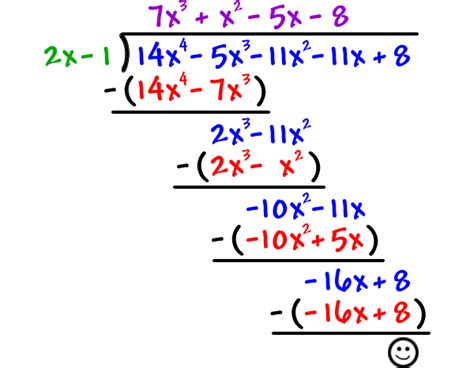
Table of Contents
Polynomial Long Division Calculator with Steps: A Comprehensive Guide
Polynomial long division is a fundamental concept in algebra, used to simplify complex polynomial expressions and solve various mathematical problems. While the process can be tedious and prone to errors, especially with higher-degree polynomials, utilizing a polynomial long division calculator with step-by-step solutions can significantly improve accuracy and understanding. This guide will delve into the intricacies of polynomial long division, explaining the process, highlighting common pitfalls, and demonstrating how to effectively use a calculator to streamline the process.
Understanding Polynomial Long Division
Before diving into the use of calculators, let's solidify our understanding of the underlying mathematical principle. Polynomial long division is analogous to the long division you learned in elementary school, but instead of dividing numbers, we divide polynomials. The process involves dividing a dividend (the polynomial being divided) by a divisor (the polynomial doing the dividing) to obtain a quotient (the result of the division) and a remainder (any leftover portion). The general form can be expressed as:
Dividend = Quotient × Divisor + Remainder
For example, consider dividing the polynomial x² + 5x + 6 by x + 2. Here, x² + 5x + 6 is the dividend and x + 2 is the divisor.
The Step-by-Step Manual Process
Let's manually perform the long division to illustrate the process.
-
Setup: Arrange both the dividend and the divisor in descending order of powers. If any powers are missing, include them with a coefficient of 0 (e.g., x² + 6 becomes x² + 0x + 6).
-
Divide the leading terms: Divide the leading term of the dividend (x²) by the leading term of the divisor (x). This gives us x. Write this as the first term of the quotient.
-
Multiply: Multiply the obtained quotient term (x) by the entire divisor (x + 2). This gives us x² + 2x.
-
Subtract: Subtract the result (x² + 2x) from the dividend (x² + 5x + 6). This leaves us with 3x + 6.
-
Bring down: Bring down the next term from the dividend (which is 6 in this case).
-
Repeat: Repeat steps 2-5. Divide the leading term of the new polynomial (3x) by the leading term of the divisor (x), which gives us 3. This is the next term in the quotient. Multiply 3 by (x + 2) to get 3x + 6. Subtract this from 3x + 6, resulting in a remainder of 0.
Therefore, x² + 5x + 6 divided by x + 2 equals x + 3 with a remainder of 0.
Utilizing a Polynomial Long Division Calculator
While the manual method is educational, it can be cumbersome, especially for higher-degree polynomials or those with more complex coefficients. This is where a polynomial long division calculator becomes invaluable. Many online calculators are available that perform this task efficiently and accurately.
Key Features to Look For:
- Step-by-step explanation: A good calculator will not only provide the final answer but also show each step of the division process, mirroring the manual method explained above. This allows you to follow along and understand the calculation.
- Handling of complex numbers: Some calculators support complex numbers as coefficients, enhancing their versatility.
- Clear input interface: The calculator should have a user-friendly interface that simplifies entering polynomials. Look for calculators that allow you to input polynomials in standard algebraic notation.
- Different output formats: The output should be easily readable, providing the quotient and remainder clearly.
Interpreting Calculator Results
Once you input the dividend and divisor into the calculator, it will process the division and present the results. Ensure you understand the following aspects of the output:
- Quotient: This is the polynomial obtained by dividing the dividend by the divisor. It represents the primary result of the division.
- Remainder: The remainder is the leftover portion after dividing as much as possible. If the remainder is 0, the divisor is a factor of the dividend.
- Verification: After obtaining the results, you can verify the calculation using the equation: Dividend = Quotient × Divisor + Remainder. Plugging the values in should always result in a true statement.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even with a calculator, some common mistakes can occur. Understanding these helps you effectively interpret the calculator's results and avoid misinterpretations.
- Incorrect order of terms: Always arrange the terms in both the dividend and divisor in descending order of their exponents. Failure to do so can lead to incorrect intermediate results.
- Sign errors: Subtracting polynomials correctly involves distributing the negative sign. Pay close attention to sign changes during the subtraction steps. Calculators generally handle this correctly, but verifying these steps manually can be beneficial for understanding.
- Misinterpretation of the remainder: The remainder might not always be zero. Understanding the meaning of a non-zero remainder is important, as it signifies that the divisor is not a factor of the dividend.
- Input errors: Double-check the input polynomials before submitting them to the calculator. A small mistake in typing can significantly affect the results.
Advanced Applications of Polynomial Long Division
Beyond the basic application, polynomial long division has various advanced uses in algebra and other fields:
- Finding factors: If the remainder is 0, the divisor is a factor of the dividend. This is crucial in factoring polynomials and solving equations.
- Partial fraction decomposition: Polynomial long division is often a preliminary step in decomposing rational functions into simpler fractions, simplifying integration and other calculus operations.
- Synthetic division: For divisors of the form (x - c), synthetic division provides a more efficient method. While calculators generally handle both methods, understanding synthetic division can provide insights into the process.
- Solving polynomial equations: By factoring polynomials using long division, you can find the roots of polynomial equations.
Conclusion
Polynomial long division, while potentially complex, is a fundamental algebraic tool. Using a polynomial long division calculator with step-by-step solutions greatly simplifies the process and minimizes errors, especially for more complex problems. Understanding the underlying principles and being aware of common mistakes allows for a more confident and accurate use of these calculators. Remember to always verify the results and utilize the calculator as a tool to enhance your understanding, not replace it. By combining manual understanding with the efficiency of calculators, you can master this crucial algebraic technique and apply it effectively in diverse mathematical contexts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Is 62 Kg In Pounds
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is 60 Pounds
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 105 Days From Today
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Pounds Are In 48 Ounces
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Pounds Are In 24 Ounces
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Polynomial Long Division Calculator With Steps . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
