Partial Derivative X Y Z Calculator
Greels
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
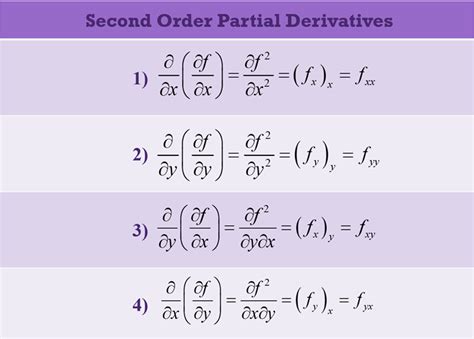
Table of Contents
Partial Derivative x y z Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
The world of multivariable calculus can seem daunting, particularly when grappling with partial derivatives involving multiple variables like x, y, and z. Understanding these derivatives is crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, economics, and machine learning. While the underlying mathematical concepts require a firm grasp of calculus principles, the practical application often involves tedious calculations. This is where a partial derivative x y z calculator becomes invaluable. This article delves into the intricacies of partial derivatives, explains how to calculate them manually, and explores the benefits and uses of a partial derivative calculator, focusing on those handling three variables (x, y, and z).
Understanding Partial Derivatives
Before diving into calculators, let's solidify our understanding of partial derivatives. A partial derivative measures the rate of change of a function with respect to one of its variables, while holding all other variables constant. This contrasts with total derivatives, which consider the simultaneous change of all variables.
Imagine a function f(x, y, z). The partial derivative with respect to x, denoted as ∂f/∂x, represents how the function's value changes as x changes infinitesimally, while y and z remain fixed. Similarly, ∂f/∂y and ∂f/∂z represent the rates of change with respect to y and z, respectively, holding other variables constant.
Example: Calculating Partial Derivatives Manually
Let's consider the function: f(x, y, z) = x²y + 2xz + yz²
To find the partial derivative with respect to x (∂f/∂x), we treat y and z as constants:
∂f/∂x = 2xy + 2z
To find the partial derivative with respect to y (∂f/∂y), we treat x and z as constants:
∂f/∂y = x² + z²
Finally, to find the partial derivative with respect to z (∂f/∂z), we treat x and y as constants:
∂f/∂z = 2x + 2yz
Why Use a Partial Derivative x y z Calculator?
While calculating partial derivatives for simple functions like the example above is manageable by hand, the complexity increases dramatically with more intricate functions. Higher-order partial derivatives (like ∂²f/∂x², ∂²f/∂x∂y, etc.) further amplify the computational burden. This is where a partial derivative x y z calculator proves its worth:
-
Time Savings: Calculators significantly reduce the time spent on manual calculations, allowing you to focus on interpreting the results and applying them to your problem.
-
Accuracy: Manual calculations are prone to errors, especially with complex functions or higher-order derivatives. Calculators minimize these errors, providing accurate results consistently.
-
Efficiency: For large-scale projects or iterative calculations, a calculator streamlines the process, increasing overall efficiency.
-
Accessibility: Calculators make advanced calculus concepts accessible to a wider audience, including students, researchers, and professionals who may not have extensive mathematical expertise.
-
Handling Complex Functions: Calculators can effortlessly handle functions involving trigonometric, exponential, logarithmic, and other special functions, which are often challenging to compute manually.
Features of a Powerful Partial Derivative Calculator
A robust partial derivative x y z calculator should offer several key features:
-
Input Flexibility: It should accept a wide range of function notations, including common mathematical symbols and operators.
-
Variable Handling: Clearly supports multiple variables (x, y, z, and potentially more).
-
Higher-Order Derivatives: Ability to calculate higher-order partial derivatives.
-
Step-by-Step Solutions: Many advanced calculators offer step-by-step solutions, providing valuable insights into the calculation process. This is crucial for learning and understanding the underlying mathematics.
-
Symbolic Differentiation: The ability to perform symbolic differentiation, meaning it provides the derivative as a mathematical expression rather than just a numerical value. This allows for deeper analysis and understanding of the function's behavior.
-
User-Friendly Interface: A well-designed interface is essential for intuitive usage and quick results.
-
Visualization Tools (Optional): Some advanced calculators incorporate visualization tools, allowing you to see graphical representations of the function and its derivatives. This can enhance comprehension, particularly for visualizing multivariable functions in three dimensions.
Applications of Partial Derivatives
Partial derivatives are fundamental in numerous fields:
-
Physics: Calculating rates of change in physical systems, such as heat flow (heat equation), fluid dynamics (Navier-Stokes equations), and electromagnetism (Maxwell's equations).
-
Engineering: Optimizing designs, analyzing stress and strain in materials, and modeling dynamic systems.
-
Economics: Analyzing marginal productivity, utility functions, and equilibrium points in economic models.
-
Machine Learning: Calculating gradients in optimization algorithms (like gradient descent) for training machine learning models. This is crucial for finding optimal parameters within complex models.
-
Computer Graphics: Used in shading calculations, surface normal calculations, and other aspects of creating realistic 3D images.
-
Image Processing: Partial derivatives are used in edge detection algorithms to identify regions of rapid change in an image.
Beyond x, y, and z: Handling More Variables
While many applications involve three variables (x, y, z), the principles of partial derivatives extend to functions with any number of variables. A sophisticated calculator should be able to handle functions with an arbitrary number of variables. The concept remains the same: we differentiate with respect to one variable, holding all others constant.
Choosing the Right Partial Derivative Calculator
The best partial derivative x y z calculator for you will depend on your specific needs and technical proficiency. Consider the features mentioned earlier when making your choice. Some calculators are simple online tools, while others are part of larger mathematical software packages. For educational purposes, a calculator with step-by-step solutions is beneficial. For professional applications where speed and accuracy are paramount, a highly efficient calculator integrated into a broader workflow is preferred.
Conclusion
Partial derivatives are an essential component of multivariable calculus and find broad application across diverse fields. While manual calculation is feasible for simple functions, a partial derivative x y z calculator is invaluable for tackling complex functions and higher-order derivatives efficiently and accurately. By understanding the underlying mathematical concepts and leveraging the power of a suitable calculator, you can effectively utilize partial derivatives to solve a wide array of problems in various disciplines. Choosing the right calculator depends on your specific requirements, so careful consideration of the features and functionalities is crucial for optimal use.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Is 140 Mm
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Kg In 22 Pounds
Mar 26, 2025
-
98 Kilos Is How Many Pounds
Mar 26, 2025
-
67 In Is How Many Feet
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 54 Kilos In Pounds
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Partial Derivative X Y Z Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
