Multiplying And Dividing Rational Expressions Solver
Greels
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
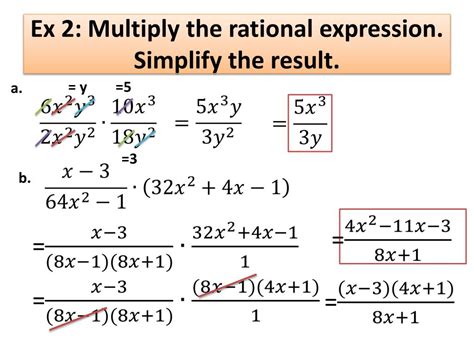
Table of Contents
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Solver: A Comprehensive Guide
Rational expressions, the algebraic counterparts of fractions, often present challenges for students. Mastering the art of multiplying and dividing them requires a solid understanding of fundamental algebraic principles. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, equipping you with the skills to confidently tackle even the most complex rational expression problems. We'll cover everything from simplifying individual expressions to solving complex equations involving multiplication and division. By the end, you'll have the tools to become a proficient solver of rational expressions.
Understanding Rational Expressions
Before diving into the operations, let's solidify our understanding of what rational expressions are. A rational expression is simply a fraction where the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example, (3x² + 2x)/(x - 5) is a rational expression. Remember, polynomials are expressions involving variables and constants, combined using addition, subtraction, and multiplication, with non-negative integer exponents on the variables.
Key Concepts Before We Begin:
- Factoring: Factoring polynomials is crucial for simplifying rational expressions. Being fluent in factoring techniques like greatest common factor (GCF), difference of squares, perfect square trinomials, and grouping is paramount.
- Simplifying Fractions: The core principle of simplifying rational expressions mirrors simplifying numerical fractions. You cancel out common factors from the numerator and denominator.
- Restrictions: Remember that the denominator of a rational expression can never be zero. This means certain values of the variable are excluded from the domain. Identifying these restrictions is vital, especially when simplifying or solving equations.
Multiplying Rational Expressions
Multiplying rational expressions is straightforward: multiply the numerators together and multiply the denominators together. However, the real skill lies in simplifying the resulting expression to its lowest terms.
Step-by-Step Guide to Multiplying Rational Expressions:
-
Factor Completely: The first and most critical step is to factor both the numerators and denominators of the expressions involved. This often requires using various factoring techniques mentioned earlier. Finding common factors will significantly simplify the process.
-
Multiply Numerators and Denominators: Once factored, multiply the numerators together to form a new numerator and multiply the denominators together to form a new denominator.
-
Simplify: This is where the true simplification occurs. Look for common factors in the numerator and denominator of the resulting expression. Cancel out these common factors to simplify the expression to its lowest terms. Remember to explicitly state any restrictions on the variable resulting from setting the denominator equal to zero at any stage of the calculation.
Example:
Let's multiply (x² - 4)/(x + 3) and (x + 3)/(x + 2).
-
Factor: (x - 2)(x + 2)/(x + 3) * (x + 3)/(x + 2)
-
Multiply: [(x - 2)(x + 2)(x + 3)] / [(x + 3)(x + 2)]
-
Simplify: (x - 2) (Note: x ≠ -3, x ≠ -2)
The simplified expression is (x - 2), with the restrictions x ≠ -3 and x ≠ -2, because those values would make the original denominators zero.
Dividing Rational Expressions
Dividing rational expressions involves a slightly more intricate process than multiplication. It requires inverting the second expression (the divisor) and then multiplying.
Step-by-Step Guide to Dividing Rational Expressions:
-
Invert the Divisor: The first step is to invert (flip) the second rational expression, turning the division problem into a multiplication problem.
-
Multiply: Follow the steps for multiplying rational expressions outlined above: factor completely, multiply numerators and denominators, and simplify by cancelling common factors. Always remember to state the restrictions.
Example:
Let's divide (x² - 9)/(x + 5) by (x + 3)/(x - 1).
-
Invert: (x² - 9)/(x + 5) * (x - 1)/(x + 3)
-
Factor: [(x - 3)(x + 3)]/(x + 5) * (x - 1)/(x + 3)
-
Multiply and Simplify: [(x - 3)(x + 3)(x - 1)]/[(x + 5)(x + 3)] = (x - 3)(x - 1)/(x + 5) (Note: x ≠ -5, x ≠ -3)
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
While the basic steps outlined above cover most scenarios, let's delve into some more advanced situations you might encounter:
Complex Rational Expressions:
Complex rational expressions involve rational expressions within other rational expressions. To simplify these, treat the numerator and denominator as separate rational expressions, simplifying them individually before performing the division.
Expressions with Higher-Degree Polynomials:
With higher-degree polynomials, factoring can become more complex. You may need to utilize techniques like synthetic division or the rational root theorem to find factors.
Expressions Involving Multiple Variables:
The principles remain the same when dealing with expressions containing multiple variables. Factor completely, keeping track of all variables and their respective restrictions.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
Rational expressions aren't just abstract mathematical concepts; they have practical applications across various fields:
- Physics: Describing relationships between variables like velocity, acceleration, and time often involves rational expressions.
- Engineering: In designing circuits or structures, calculations often involve manipulating rational expressions.
- Economics: Modeling economic phenomena frequently uses rational functions to represent relationships between variables like supply, demand, and price.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
Many common mistakes arise when working with rational expressions. Here are a few to watch out for:
- Forgetting to Factor Completely: Always ensure you factor both the numerators and denominators completely before multiplying or simplifying.
- Incorrectly Cancelling Terms: You can only cancel common factors, not terms. For example, (x + 2) can be canceled with another (x + 2), but not just a '2' from within the parentheses.
- Ignoring Restrictions: Always identify and state the restrictions on the variable to prevent division by zero. This is crucial for maintaining the mathematical integrity of your solutions.
Conclusion: Mastering Rational Expressions
Multiplying and dividing rational expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra. While it initially may seem daunting, understanding the underlying principles of factoring and simplification makes the process manageable and even enjoyable. By carefully following the steps outlined, being meticulous with factoring and simplification, and consistently checking for restrictions, you can develop proficiency in solving these expressions and apply them to various mathematical and real-world situations. Remember practice is key—the more you work through problems, the more confident and efficient you'll become. So grab a pencil, tackle some practice problems, and soon you'll be a master of rational expressions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Is 64 Cm
Mar 25, 2025
-
7 7c 1 4c 13 3c 2
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Kg Is 240 Lbs
Mar 25, 2025
-
90 Grams Is How Many Ounces
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is 41 Inches In Feet
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Multiplying And Dividing Rational Expressions Solver . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
