Multiplication And Division Of Rational Expressions Calculator
Greels
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
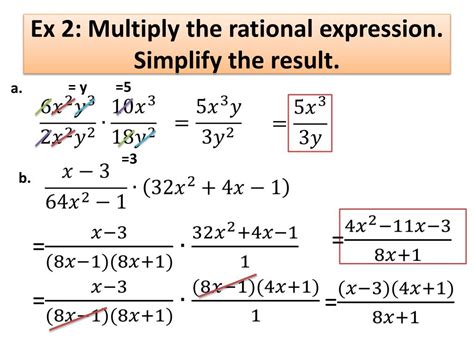
Table of Contents
Multiplication and Division of Rational Expressions Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Rational expressions, the algebraic equivalent of fractions, can often seem daunting. However, mastering the multiplication and division of these expressions is crucial for success in algebra and beyond. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, demystifying the complexities and empowering you to tackle these problems with confidence. We'll explore the underlying principles, provide step-by-step examples, and discuss the invaluable role of a multiplication and division of rational expressions calculator as a learning tool and verification aid.
Understanding Rational Expressions
Before diving into multiplication and division, let's solidify our understanding of rational expressions themselves. A rational expression is simply a ratio of two polynomials. Remember that a polynomial is an expression consisting of variables and coefficients, involving only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents.
Examples of Rational Expressions:
(x² + 2x + 1) / (x + 1)(3x - 6) / (x² - 4)5 / (x² + x)(x⁴ - 16) / (x² + 4)
Key Considerations:
-
Undefined Values: It's crucial to identify values of the variable that would make the denominator equal to zero. These values are undefined, as division by zero is impossible. For example, in the expression
(x² + 2x + 1) / (x + 1), x cannot equal -1, because this would make the denominator zero. -
Simplifying Expressions: Just like fractions, rational expressions can often be simplified by canceling common factors from the numerator and the denominator. This simplification makes calculations easier and reveals the essential structure of the expression.
Multiplication of Rational Expressions
Multiplying rational expressions is surprisingly straightforward. It follows the same basic principle as multiplying ordinary fractions: multiply the numerators together and multiply the denominators together.
Steps for Multiplying Rational Expressions:
-
Factor Completely: The first, and arguably most important step, is to factor both the numerators and the denominators of the rational expressions completely. This involves identifying common factors and expressing each polynomial as a product of simpler polynomials.
-
Multiply Numerators and Denominators: Once factored, multiply the numerators together to form a new numerator and multiply the denominators together to form a new denominator.
-
Cancel Common Factors: Look for common factors in the numerator and the denominator of the resulting expression. Cancel these factors to simplify the expression to its lowest terms.
Example:
Multiply: (x² - 4) / (x + 3) * (x + 3) / (x - 2)
-
Factor:
(x - 2)(x + 2) / (x + 3) * (x + 3) / (x - 2) -
Multiply:
(x - 2)(x + 2)(x + 3) / ((x + 3)(x - 2)) -
Cancel: The
(x + 3)and(x - 2)terms cancel out, leavingx + 2.
Therefore, the simplified result is x + 2. Remember that x cannot be 2 or -3, as these values would make the original denominators zero.
Division of Rational Expressions
Dividing rational expressions is also similar to dividing ordinary fractions. The key is to remember that dividing by a fraction is the same as multiplying by its reciprocal.
Steps for Dividing Rational Expressions:
-
Find the Reciprocal: Invert the second rational expression (the divisor), swapping its numerator and denominator.
-
Multiply: Multiply the first rational expression by the reciprocal of the second. Follow the steps for multiplication as outlined above (factor, multiply, cancel).
Example:
Divide: (x² + 5x + 6) / (x + 1) ÷ (x + 3) / (x² - 1)
-
Find the Reciprocal: The reciprocal of
(x + 3) / (x² - 1)is(x² - 1) / (x + 3) -
Multiply:
(x² + 5x + 6) / (x + 1) * (x² - 1) / (x + 3) -
Factor:
(x + 2)(x + 3) / (x + 1) * (x - 1)(x + 1) / (x + 3) -
Multiply and Cancel:
(x + 2)(x + 3)(x - 1)(x + 1) / (x + 1)(x + 3)The(x + 1)and(x + 3)terms cancel, leaving(x + 2)(x - 1).
Therefore, the simplified result is (x + 2)(x - 1) or x² + x - 2. Remember that x cannot be -1, -3, or 1.
The Role of a Multiplication and Division of Rational Expressions Calculator
While understanding the underlying principles is paramount, a multiplication and division of rational expressions calculator can serve as a powerful tool for:
-
Verification: After completing a problem manually, use a calculator to verify your answer. This helps identify any errors in your calculations.
-
Complex Problems: For problems involving very large or complex polynomials, a calculator can streamline the process significantly. It handles the factoring and simplification steps efficiently.
-
Learning Aid: By inputting problems and observing the step-by-step solutions provided by the calculator, you can gain a deeper understanding of the techniques involved.
-
Exploring Different Approaches: A calculator can help explore alternative methods for solving problems and compare the results.
Important Note: While a calculator is an invaluable tool, it's crucial to focus on understanding the underlying mathematical concepts first. Over-reliance on calculators can hinder your ability to solve problems independently.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
-
Least Common Denominator (LCD): When dealing with complex expressions, finding the least common denominator can be essential for simplifying and performing addition or subtraction after multiplication or division.
-
Partial Fraction Decomposition: For more intricate rational expressions, partial fraction decomposition is a powerful technique used to break down a complex fraction into simpler components. This is often helpful in calculus and other advanced mathematical contexts.
-
Complex Numbers: In some cases, you might encounter rational expressions that involve complex numbers (numbers containing the imaginary unit 'i'). The principles of multiplication and division remain the same, but the calculations may involve handling complex conjugates.
-
Restrictions on Variables: Always remember to state any restrictions on the variables to avoid division by zero. This is a critical aspect of working with rational expressions that must not be overlooked.
Conclusion
Mastering multiplication and division of rational expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra. By understanding the process of factoring, multiplying, canceling common factors, and finding reciprocals, you can effectively tackle even the most complex rational expressions. Remember to use a calculator as a valuable verification tool and learning aid, but prioritize developing a strong conceptual understanding. With practice and a structured approach, you will become proficient in manipulating these algebraic structures and excel in your mathematical studies. Through consistent practice and a strategic use of tools like calculators, you can build a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Never hesitate to explore further resources and practice problems to reinforce your understanding and skill development.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 210 Cm
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Much Is 170 Kg In Pounds
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Long Is 48 Inches In Feet
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 37 Kg In Pounds
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 180 Mm In Inches
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Multiplication And Division Of Rational Expressions Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
