Math Word Problem Solver With Steps
Greels
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
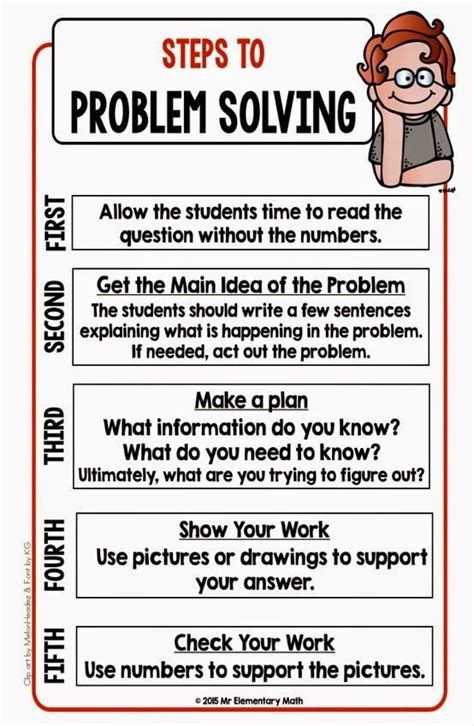
Table of Contents
Math Word Problem Solver with Steps: A Comprehensive Guide
Solving math word problems can be a daunting task for many, but with a systematic approach and the right techniques, you can conquer even the most complex problems. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the tools and strategies to become a proficient math word problem solver. We'll explore various problem-solving techniques, delve into specific examples, and offer tips to enhance your overall problem-solving skills.
Understanding the Problem: The Foundation of Success
Before diving into calculations, the most crucial step is to thoroughly understand the problem itself. This involves:
1. Reading Carefully and Identifying Key Information:
Read the problem slowly and attentively. Don't rush through it. Identify the key pieces of information: what is given, what is unknown, and what relationships exist between the given and unknown quantities. Underline or highlight important numbers, keywords, and phrases. This focused reading helps prevent misinterpretations and sets the stage for a successful solution.
2. Visualizing the Problem:
Many word problems benefit from visualization. Draw a diagram, chart, or picture to represent the information provided. This visual representation can help clarify relationships between variables and make the problem easier to understand. For geometry problems, a sketch is often essential. For problems involving rates, a timeline can be very helpful.
3. Defining Variables:
Assign variables (usually letters like x, y, z) to represent the unknown quantities. Clearly define what each variable represents. For example, "Let x represent the number of apples" or "Let y represent the speed of the car." This step formalizes the problem and makes the algebraic manipulation easier.
Employing Effective Problem-Solving Strategies
Once you have a clear grasp of the problem, you can employ various strategies to solve it. Here are some of the most effective:
1. The Four-Step Problem-Solving Process:
This classic method breaks down problem-solving into four manageable steps:
- Understand: Carefully read and understand the problem. Identify the knowns, unknowns, and the relationships between them.
- Plan: Develop a strategy to solve the problem. This might involve choosing an appropriate formula, drawing a diagram, or creating a table.
- Solve: Execute your plan, showing all your work clearly and neatly. Check your calculations at each step to minimize errors.
- Check: Review your answer to ensure it makes sense in the context of the problem. Does the answer seem reasonable? Are the units correct?
2. Working Backwards:
Some problems can be solved more efficiently by working backward from the answer. If the problem gives you the final result and asks for an initial value, start with the final result and reverse the operations to find the initial value.
3. Guess and Check:
This method involves making an educated guess, checking if it satisfies the conditions of the problem, and refining your guess based on the results. It’s particularly useful when dealing with problems that don't readily lend themselves to algebraic solutions.
4. Using Algebra:
Algebraic methods are powerful tools for solving many word problems. Translate the words into mathematical equations, solve the equations, and interpret the results in the context of the problem. This often involves using variables, forming equations based on the given information, and solving for the unknowns.
5. Utilizing Formulas:
Many word problems involve standard formulas. For example, problems related to distance, rate, and time often use the formula: Distance = Rate × Time. Recognizing and applying the appropriate formula can significantly simplify the solution process. Remember to always identify the known and unknown variables within the formula before solving.
Examples and Solutions: Putting it all Together
Let's examine some examples to illustrate the application of these techniques:
Example 1: Age Problem
-
Problem: John is twice as old as his son. In five years, the sum of their ages will be 55. How old is John now?
-
Solution:
- Define variables: Let x represent the son's current age. John's current age is 2x.
- Formulate equations: In five years, the son's age will be x + 5, and John's age will be 2x + 5. The sum of their ages will be (x + 5) + (2x + 5) = 55.
- Solve the equation: 3x + 10 = 55 => 3x = 45 => x = 15.
- Interpret the result: The son is currently 15 years old. John is 2 * 15 = 30 years old.
Example 2: Mixture Problem
-
Problem: A chemist needs to mix a 20% acid solution with a 50% acid solution to obtain 10 liters of a 30% acid solution. How many liters of each solution should be mixed?
-
Solution:
- Define variables: Let x represent the liters of 20% solution and y represent the liters of 50% solution.
- Formulate equations: x + y = 10 (total volume) and 0.20x + 0.50y = 0.30(10) (acid concentration).
- Solve the system of equations: You can use substitution or elimination methods to solve for x and y. Solving gives x = 5 and y = 5.
- Interpret the result: The chemist needs to mix 5 liters of the 20% solution and 5 liters of the 50% solution.
Example 3: Rate Problem
-
Problem: A train travels 300 miles at a speed of 60 mph. How long does the trip take?
-
Solution:
- Identify the formula: Distance = Rate × Time
- Identify the knowns: Distance = 300 miles, Rate = 60 mph
- Solve for the unknown: Time = Distance / Rate = 300 miles / 60 mph = 5 hours.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
As you progress, you might encounter more complex word problems requiring advanced techniques:
- Inequalities: Problems involving "at least," "at most," "less than," or "greater than" require the use of inequalities.
- Systems of Equations: Problems with multiple unknowns often require solving a system of equations simultaneously.
- Quadratic Equations: Some problems lead to quadratic equations that need to be solved using factoring, the quadratic formula, or completing the square.
Tips for Improving Your Word Problem-Solving Skills
- Practice Regularly: The key to mastering word problems is consistent practice. The more problems you solve, the better you'll become at identifying patterns and applying appropriate strategies.
- Seek Help When Needed: Don't hesitate to ask for help from teachers, tutors, or classmates if you're struggling with a particular problem.
- Break Down Complex Problems: Divide complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts.
- Review Your Mistakes: Analyze your mistakes carefully to understand where you went wrong and learn from your errors.
- Use Multiple Approaches: Sometimes, trying different solution methods can help you gain a deeper understanding of the problem.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Problem Solving
Solving math word problems is a skill that develops over time with practice and the right approach. By understanding the problem thoroughly, choosing the appropriate strategy, and meticulously checking your work, you can confidently tackle even the most challenging problems. Remember to break down the problem, visualize the situation, and utilize the various techniques outlined in this guide. With dedication and persistence, you'll become a proficient math word problem solver, enhancing your mathematical abilities and boosting your confidence.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Parallel Line And Perpendicular Line Calculator
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Much 145 Pounds Is In Kilograms
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is 160 Kg In Pounds
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Kilos Is 126 Pounds
Mar 25, 2025
-
3 4 Kg Is How Many Pounds
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Math Word Problem Solver With Steps . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
