Inverse Laplace Transform Calculator Step-by Step
Greels
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
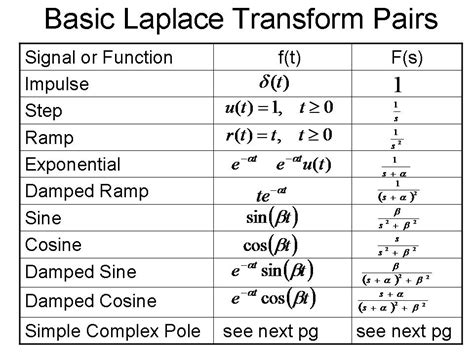
Table of Contents
Inverse Laplace Transform Calculator: A Step-by-Step Guide
The Laplace transform is a powerful mathematical tool used extensively in engineering and physics to solve differential equations. While finding the Laplace transform of a function is relatively straightforward, determining the inverse Laplace transform can be significantly more challenging. This article provides a comprehensive, step-by-step guide to understanding and utilizing inverse Laplace transform calculators, along with a deep dive into the underlying mathematical principles. We’ll explore various methods, including partial fraction decomposition, convolution theorem, and the use of tables, enabling you to confidently tackle even the most complex inverse Laplace transforms.
Understanding the Laplace Transform and its Inverse
Before delving into the practical application of inverse Laplace transform calculators, let's briefly review the fundamental concepts. The Laplace transform, denoted as L{f(t)}, transforms a function of time, f(t), into a function of a complex variable, s, denoted as F(s). This transformation often simplifies the solution of differential equations by converting them into algebraic equations.
The inverse Laplace transform, denoted as L⁻¹{F(s)}, performs the reverse operation, transforming the function F(s) back into the original time-domain function f(t). This is crucial because the solution obtained in the s-domain often needs to be translated back to the time domain to have practical meaning.
The Role of Inverse Laplace Transform Calculators
Inverse Laplace transform calculators are invaluable tools for simplifying the often tedious process of finding the inverse Laplace transform. These calculators leverage various algorithms and techniques to efficiently compute the inverse transform, significantly reducing the time and effort involved in manual calculations. While these calculators are incredibly helpful, understanding the underlying mathematical principles remains crucial for interpreting the results and ensuring accuracy.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using an Inverse Laplace Transform Calculator
While the specific interface may vary slightly depending on the calculator used, the general steps involved are consistently similar:
Step 1: Input the Laplace Transform Function:
Enter the Laplace transform function, F(s), accurately into the calculator's input field. Pay close attention to syntax and notation, ensuring correct use of parentheses, exponents, and mathematical operators. For instance, if your function is (s+1)/(s² + 2s + 5), input it precisely as such. Common mistakes include incorrect placement of parentheses or misinterpreting the order of operations.
Step 2: Select the Method (If Applicable):
Some advanced calculators offer the option to select the method used for computing the inverse transform. Options may include partial fraction decomposition, convolution theorem, or other techniques. Choosing the appropriate method can sometimes improve calculation speed and accuracy. However, for many standard functions, the calculator will automatically select the most efficient algorithm.
Step 3: Execute the Calculation:
Click the "Calculate" or equivalent button to initiate the computation. The calculator will use its internal algorithms to determine the inverse Laplace transform. Depending on the complexity of the function, this process might take a few seconds.
Step 4: Interpret the Results:
The calculator will display the resulting inverse Laplace transform, f(t). Carefully examine the output to ensure it's consistent with your expectations and the context of the problem. Understand that the output might be presented in various forms, such as a simplified algebraic expression or a piecewise function, depending on the nature of the original Laplace transform.
Step 5: Verify the Result (Optional but Highly Recommended):
For critical applications, it's highly recommended to verify the result obtained from the calculator. You can do this by manually calculating the Laplace transform of the obtained f(t) and comparing it to the original F(s). While this step may be time-consuming, it offers a crucial check against potential errors, especially in complex scenarios.
Common Methods Used by Inverse Laplace Transform Calculators
Inverse Laplace transform calculators often employ several techniques to compute the inverse transform. Understanding these methods provides a deeper insight into the calculator's functionality and helps in interpreting the results:
1. Partial Fraction Decomposition:
This is one of the most widely used methods for simpler rational functions. The method involves decomposing a rational function (a ratio of two polynomials) into a sum of simpler fractions. These simpler fractions have inverse Laplace transforms that are readily available in tables or are easily calculable. For example, a function like (s+1)/(s² + 2s + 5) can be decomposed using partial fractions to obtain a sum of terms whose inverse Laplace transforms are easily determined.
2. Convolution Theorem:
The convolution theorem provides an elegant way to find the inverse Laplace transform of a product of two Laplace transforms. It states that the inverse Laplace transform of a product of two functions, F(s)G(s), is the convolution of their individual inverse Laplace transforms, f(t) * g(t). This simplifies calculations when dealing with products of Laplace transforms, allowing the calculator to handle more complex functions.
3. Table Lookup:
Many inverse Laplace transform calculators utilize extensive tables of Laplace transforms and their inverses. If the input function or its simplified form is found in the table, the calculator directly retrieves the corresponding inverse transform, providing a rapid and accurate solution. These tables typically contain common functions and their respective Laplace transforms, enabling quick lookups for many frequently encountered problems.
4. Numerical Methods:
For complex or non-standard functions, some inverse Laplace transform calculators might employ numerical methods like numerical inversion algorithms. These algorithms approximate the inverse transform using numerical techniques, providing an approximate but often sufficiently accurate solution. Such methods are particularly helpful for functions that cannot be easily handled using analytical methods.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
For particularly complex inverse Laplace transforms, more advanced techniques might be necessary:
-
Bromwich Integral: This is the most general method for finding the inverse Laplace transform. It involves a complex contour integral, which is computationally intensive and typically not directly used by most calculators.
-
Residue Theorem: Related to the Bromwich integral, this method utilizes complex analysis to compute the inverse transform using the residues of the integrand.
-
Power Series Expansion: Expanding the function as a power series can sometimes simplify the inversion process, particularly for functions that are not easily decomposable using partial fractions.
Tips for Effective Use of Inverse Laplace Transform Calculators
-
Double-check your input: Ensure that the function entered is correct, including parentheses, exponents, and operators. A small error in the input can lead to a significantly inaccurate or erroneous result.
-
Understand the limitations: While powerful, calculators have limitations. Extremely complex or unconventional functions might not yield accurate results.
-
Learn the underlying principles: Understanding the methods used by the calculator helps you interpret the output and identify potential issues.
-
Verify your results: Whenever possible, independently verify the result obtained from the calculator using manual calculation or other methods to ensure accuracy.
-
Explore different calculators: Different calculators might offer different features and capabilities. Experimenting with several calculators can be helpful in obtaining accurate results, especially for challenging problems.
Conclusion
Inverse Laplace transform calculators are invaluable tools for engineers, physicists, and mathematicians working with differential equations. By understanding the underlying mathematical principles and utilizing the calculator effectively, you can significantly simplify the process of finding the inverse Laplace transform. Remember to always carefully input the function, interpret the results critically, and verify the solution whenever possible to ensure accuracy and a thorough understanding of the problem. Mastering the use of these calculators, alongside a robust understanding of Laplace transforms, is key to efficient and accurate problem-solving in many scientific and engineering applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Is 120 Mm
Mar 21, 2025
-
115 Lbs Is How Many Kg
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Pounds Is 1 5 Kg
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Tall In Feet Is 56 Inches
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Lbs Is 110 Kg
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Inverse Laplace Transform Calculator Step-by Step . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
