Finding The Area Under The Curve Calculator
Greels
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
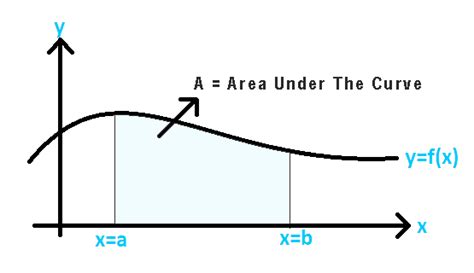
Table of Contents
Finding the Area Under the Curve Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the area under a curve is a fundamental concept in calculus with widespread applications in various fields, from physics and engineering to economics and statistics. Manually calculating this area can be complex and time-consuming, especially for intricate curves. This is where the area under the curve calculator becomes an invaluable tool. This comprehensive guide explores the concept, its applications, the different methods used by calculators, and how to effectively utilize these tools.
What is the Area Under the Curve?
The area under a curve, more formally known as definite integral, represents the area bounded by a curve, the x-axis, and two vertical lines corresponding to the lower and upper limits of integration. This area provides crucial information about the accumulated quantity represented by the curve. For example:
- Velocity-Time Graph: The area under a velocity-time graph represents the total distance traveled.
- Acceleration-Time Graph: The area represents the change in velocity.
- Force-Displacement Graph: The area represents the work done.
- Probability Density Function: The area under the curve represents the probability of a random variable falling within a specified range.
Methods for Calculating the Area Under the Curve
Calculating the area under the curve involves several mathematical techniques, and area under the curve calculators employ these to provide accurate results. The most common methods include:
1. Numerical Integration Techniques:
Numerical integration methods approximate the area under the curve by dividing the area into smaller shapes (rectangles, trapezoids, etc.) and summing their areas. These methods are particularly useful when dealing with functions that are difficult or impossible to integrate analytically. Common numerical integration techniques used by calculators include:
- Rectangle Rule (Riemann Sum): This is a basic method that approximates the area using rectangles. Accuracy improves as the width of the rectangles decreases (more rectangles are used).
- Trapezoidal Rule: This method uses trapezoids instead of rectangles, providing a more accurate approximation, especially for curves with significant curvature.
- Simpson's Rule: This method uses parabolic arcs to approximate the curve, resulting in even higher accuracy than the trapezoidal rule.
- Gaussian Quadrature: This sophisticated method strategically places points within the integration interval to achieve high accuracy with fewer evaluations of the function.
2. Analytical Integration (Symbolic Integration):
Analytical integration involves finding an antiderivative (indefinite integral) of the function and evaluating it at the limits of integration. This method yields an exact result, but it's only possible for functions with known antiderivatives. Many calculators can perform symbolic integration, but limitations exist for complex functions.
3. Monte Carlo Integration:
This method uses random sampling to estimate the area under the curve. Points are randomly generated within a bounding rectangle encompassing the curve, and the ratio of points falling under the curve to the total number of points approximates the area. This method is particularly useful for high-dimensional integrals or complex functions.
Choosing the Right Area Under the Curve Calculator
The best area under the curve calculator for your needs depends on several factors:
- Type of Function: Some calculators are specifically designed for specific types of functions (e.g., polynomials, trigonometric functions, exponential functions).
- Accuracy Requirements: The required level of accuracy influences the choice of numerical integration method. High-accuracy applications may require more sophisticated methods like Simpson's rule or Gaussian quadrature.
- Complexity of the Function: For complex functions, numerical integration methods are generally necessary. Analytical integration might fail or be excessively difficult.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface is crucial, especially for those unfamiliar with calculus or numerical methods. The calculator should provide clear input fields, options for selecting integration methods, and easy-to-understand output.
Applications of Area Under the Curve Calculations
The applications of calculating the area under the curve are vast and span multiple disciplines:
1. Physics and Engineering:
- Calculating work done: In mechanics, the area under a force-displacement curve represents the work done by the force.
- Determining total distance: The area under a velocity-time graph represents the total distance traveled.
- Finding the total charge: The area under a current-time graph represents the total charge that has passed through a point.
- Analyzing signal processing: In signal processing, the area under a signal's power spectral density function represents the total power of the signal.
2. Economics and Finance:
- Calculating consumer surplus: In economics, the area under a demand curve and above the market price represents the consumer surplus.
- Determining producer surplus: The area under the market price and above the supply curve represents the producer surplus.
- Analyzing financial data: Area under curves can be used to analyze various financial indicators, such as stock prices or interest rates.
3. Statistics and Probability:
- Calculating probabilities: The area under a probability density function (PDF) represents the probability of a random variable falling within a specific range.
- Determining cumulative distribution functions (CDFs): The area under a PDF from negative infinity to a specific point represents the CDF at that point.
- Statistical hypothesis testing: Area under curves are used in various statistical hypothesis tests, such as t-tests and z-tests.
4. Medicine and Biology:
- Analyzing drug absorption: The area under a drug concentration-time curve (AUC) reflects the extent of drug absorption.
- Analyzing growth rates: Area under curves can be used to analyze various biological growth rates, such as population growth or tumor growth.
5. Environmental Science:
- Analyzing pollution levels: The area under a pollutant concentration-time curve can represent the total exposure to the pollutant.
- Analyzing climate data: Area under curves can be used to analyze various climate data, such as temperature or rainfall.
Interpreting Results from an Area Under the Curve Calculator
The output of an area under the curve calculator typically provides the numerical value of the calculated area. It's crucial to understand the units of the result, which depend on the units of the function and the x-axis. For example:
- Velocity-Time Graph (m/s vs. s): The area has units of meters (m), representing the total distance.
- Force-Displacement Graph (N vs. m): The area has units of Joules (J), representing the work done.
Always ensure you understand the context of your calculation and the units involved to accurately interpret the results. Visualizing the area under the curve alongside the numerical output can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the results.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
For more complex scenarios, advanced techniques might be necessary:
- Multiple Integrals: Calculators can handle double and triple integrals for finding volumes or other multi-dimensional quantities.
- Improper Integrals: Integrals with infinite limits require specialized techniques to handle the convergence and divergence issues.
- Singularities: Functions with singularities (points where the function is undefined) require careful consideration during numerical integration.
Conclusion
The area under the curve calculator is a powerful tool for solving complex mathematical problems across various disciplines. By understanding the underlying mathematical principles, selecting the appropriate calculator, and interpreting the results correctly, you can leverage these tools to solve real-world problems efficiently and accurately. Remember to consider the complexity of your function, the required accuracy, and the ease of use when choosing a calculator. The abundance of online resources and calculators available makes finding and using these tools accessible to everyone, regardless of their mathematical expertise. Mastering the use of an area under the curve calculator is a valuable skill for students, researchers, and professionals alike.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Square Root Of X 2 X 4
Mar 25, 2025
-
28 Grams Is How Many Ounces
Mar 25, 2025
-
System Of Linear Equations Calculator Matrix
Mar 25, 2025
-
Cross Product Of 3 Vectors Calculator
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 58 Mm
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Finding The Area Under The Curve Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
