Finding The Area Between Two Curves Calculator
Greels
Mar 22, 2025 · 7 min read
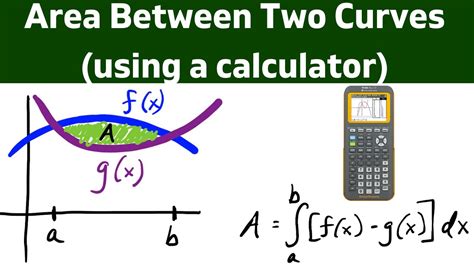
Table of Contents
Finding the Area Between Two Curves Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the area between two curves is a fundamental concept in integral calculus with widespread applications in various fields, from physics and engineering to economics and statistics. While the underlying mathematical principle is straightforward, the calculations can become complex, especially when dealing with intricate curves. This is where a finding the area between two curves calculator becomes invaluable. This comprehensive guide will delve into the theory behind calculating this area, explore the practical applications, and demonstrate how to use a calculator effectively to solve such problems.
Understanding the Concept: Area Between Two Curves
The area between two curves, say f(x) and g(x), within a specified interval [a, b] is calculated by integrating the difference between the two functions over that interval. Mathematically, this is represented as:
Area = ∫<sub>a</sub><sup>b</sup> |f(x) - g(x)| dx
The absolute value is crucial; it ensures that the area is always positive, regardless of which function is greater within a specific sub-interval. If you're working with a region where f(x) is consistently above g(x) within the interval [a, b], the absolute value signs are unnecessary and the formula simplifies to:
Area = ∫<sub>a</sub><sup>b</sup> (f(x) - g(x)) dx
However, if the curves intersect within the interval, you must carefully divide the interval into sub-intervals where one function consistently lies above the other and then integrate separately for each sub-interval, summing the results. This ensures accuracy in calculating the total area.
Identifying the Limits of Integration (a and b)
The limits of integration, a and b, define the boundaries of the region whose area you wish to compute. These limits are typically found in one of two ways:
- Given explicitly: The problem statement might directly provide the interval [a, b].
- Found through intersection points: If the interval isn't given, you need to determine where the two curves intersect. To find these points, set f(x) = g(x) and solve for x. The solutions will be your limits of integration, a and b.
Handling Complex Scenarios
Calculating the area can become complex under certain conditions:
- Multiple Intersections: If the curves intersect multiple times within the specified interval, you'll need to break the integral into multiple integrals, one for each region where one curve is consistently above the other. The intersection points will serve as the limits for each integral.
- Vertical vs. Horizontal Integration: The above formulas assume integration with respect to x. However, if it's easier to integrate with respect to y, you'll need to rewrite the functions in terms of y (i.e., x = h(y) and x = k(y)) and integrate accordingly: Area = ∫<sub>c</sub><sup>d</sup> |h(y) - k(y)| dy Where c and d are the limits of integration along the y-axis. This is particularly helpful when dealing with functions that are more easily expressed as x in terms of y.
- Functions Defined Piecewise: For functions defined piecewise, you need to apply the integration separately for each piece within the specified interval, paying careful attention to the limits of integration for each piece.
Practical Applications of Finding the Area Between Two Curves
The ability to calculate the area between two curves has numerous real-world applications:
- Economics: Calculating consumer surplus and producer surplus in market analysis. Consumer surplus represents the difference between what consumers are willing to pay and what they actually pay, while producer surplus represents the difference between the price producers receive and the cost of production. Both are represented graphically as areas between curves.
- Physics: Determining the work done by a variable force. The work done is the integral of the force function over the displacement. If the force varies with displacement, it can be represented by two curves, and the area between them represents the work done.
- Engineering: Calculating the volume of solids of revolution. The area between two curves can be rotated around an axis to generate a solid, and the volume can be calculated using integration techniques.
- Probability and Statistics: Finding the probability of an event within a given range using probability density functions. The area under the curve between two points represents the probability of the event occurring within that range.
- Computer Graphics: Rendering realistic shapes and objects by computing the area enclosed within defined boundaries. This is particularly crucial in creating smooth and accurate visual representations.
Utilizing a Finding the Area Between Two Curves Calculator
A well-designed calculator simplifies the process considerably. Here's a general guide on using such a calculator:
-
Input the Functions: Enter the equations of the two curves, f(x) and g(x), accurately. Pay close attention to the syntax and notation required by the specific calculator.
-
Specify the Limits of Integration: Input the lower and upper limits of integration (a and b). If the limits are not explicitly provided, you might need to determine the intersection points of the functions by solving f(x) = g(x) separately. Some calculators may have built-in features to automatically find these intersection points.
-
Choose the Integration Variable: Select whether the integration should be performed with respect to x or y, depending on the representation of the functions and the orientation of the area.
-
Review the Output: Once the calculator provides the result, carefully review it for reasonableness. Consider the scale of the functions and the region to ensure the area value aligns with your expectation. A significantly large or small value could indicate an error in inputting the functions or limits.
-
Handle Complex Cases: If the curves intersect multiple times, you may need to break the calculation into several steps, each representing the area in a sub-interval. Some advanced calculators have features that handle multiple intersections automatically.
Advantages of Using a Calculator
Using a calculator offers several key advantages:
- Accuracy: Calculators significantly reduce the risk of errors in complex integrations, especially when dealing with complex functions or multiple intersections.
- Speed: Calculators provide almost instantaneous results, saving valuable time.
- Efficiency: This frees up time for analysis and interpretation of the results, rather than being bogged down by manual calculations.
- Accessibility: Calculators make this powerful mathematical tool accessible to a wider audience, not just those with extensive mathematical expertise.
- Exploration: They allow for easy exploration of various scenarios by changing the functions and limits, aiding in visualizing the effect of these changes on the resulting area.
Tips for Effective Use and Troubleshooting
- Double-check your input: Carefully review the functions and limits you have entered to ensure accuracy. A small mistake can lead to a completely inaccurate result.
- Understand the limitations: Calculators can't handle all possible functions and scenarios. Be aware of the capabilities of the specific calculator you are using.
- Break down complex problems: If you encounter a problem that seems too complex, break it down into smaller, simpler problems. This modular approach reduces errors and makes the process more manageable.
- Explore different integration methods: Consider whether integration with respect to x or y is more suitable, depending on the functions involved. This can simplify the calculation substantially.
- Compare results: If possible, compare the results you obtain from a calculator with results calculated using other methods or software to verify accuracy.
Conclusion: Mastering Area Calculation
The ability to find the area between two curves is crucial across many disciplines. While the mathematical foundation is relatively straightforward, the computational aspect can be complex. By understanding the theoretical concepts and leveraging the power of a finding the area between two curves calculator, you can efficiently and accurately solve a broad range of problems, unlocking valuable insights in various fields. Remember to always double-check your inputs and understand the limitations of the tools you are using to ensure the accuracy and reliability of your results. This guide provides a solid foundation for confidently tackling these calculations and applying them in your work.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Lbs Is 140 Kg
Mar 22, 2025
-
120 Mm Is How Many Inches
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 79 In
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Inches In 16 Feet
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Inches Are In 20 Ft
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Finding The Area Between Two Curves Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
