Find The Interval Of Convergence Calculator
Greels
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
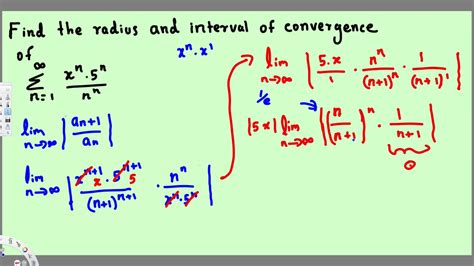
Table of Contents
Find the Interval of Convergence Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the interval of convergence for a power series can be a tedious and error-prone process. Manually calculating the radius of convergence using the ratio or root test, and then meticulously checking the endpoints for convergence, often leads to mistakes. This is where a find the interval of convergence calculator becomes an invaluable tool for students and professionals alike. This article will explore the intricacies of finding intervals of convergence, explain the underlying mathematical principles, and demonstrate how a calculator can simplify this complex task, while also highlighting potential pitfalls and offering advanced tips for using such tools effectively.
Understanding Power Series and Convergence
Before diving into the use of a calculator, let's solidify the fundamental concepts. A power series is an infinite series of the form:
∑<sub>n=0</sub><sup>∞</sup> c<sub>n</sub>(x - a)<sup>n</sup>
where:
- c<sub>n</sub> are the coefficients of the series.
- x is the variable.
- a is the center of the series.
The interval of convergence is the set of all values of x for which the power series converges. This interval is centered at a and has a certain radius, known as the radius of convergence. Outside this interval, the series diverges.
Determining the Radius of Convergence
The most common method for determining the radius of convergence (R) is the ratio test. The ratio test states that if:
lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |c<sub>n+1</sub>(x - a)<sup>n+1</sup> / c<sub>n</sub>(x - a)<sup>n</sup>| = L
then the series converges if L < 1 and diverges if L > 1. If L = 1, the test is inconclusive, and other methods must be used.
The radius of convergence is often found by solving the inequality |L| < 1 for |x - a|. This gives you an interval (a - R, a + R).
The root test offers an alternative approach:
lim<sub>n→∞</sub> |c<sub>n</sub>(x - a)<sup>n</sup>|<sup>1/n</sup> = L
Similar to the ratio test, convergence occurs if L < 1 and divergence if L > 1. The case L = 1 requires further investigation.
Checking the Endpoints
A crucial step often overlooked is checking the convergence at the endpoints of the interval (a - R, a + R). The series might converge at one, both, or neither endpoint. This requires substituting the endpoint values (a - R and a + R) back into the original power series and testing for convergence using tests like the alternating series test, p-series test, integral test, or comparison test. This determination significantly impacts the final interval of convergence.
How a Find the Interval of Convergence Calculator Works
A well-designed find the interval of convergence calculator automates these steps. It typically requires you to input the power series' coefficients and center. Internally, the calculator employs the ratio or root test (or both, offering a cross-check) to determine the radius of convergence. It then automatically checks the convergence at the endpoints, using various convergence tests as needed. The final output is the precise interval of convergence, clearly indicating whether the endpoints are included or excluded.
Advantages of Using a Calculator
- Efficiency: Saves significant time and effort, especially for complex power series.
- Accuracy: Reduces the risk of human error in calculations and endpoint checks.
- Clarity: Presents the results in a clear, concise manner.
- Learning Aid: Can be used as a learning tool to verify manual calculations and gain a deeper understanding of the concepts.
Potential Pitfalls and Limitations
While calculators are extremely helpful, it's essential to be aware of potential limitations:
- Input Errors: Incorrectly entering the coefficients or center will lead to incorrect results. Double-checking the input is crucial.
- Complex Series: Some calculators might struggle with very intricate or unusual power series.
- Understanding the Output: It's vital to understand the underlying mathematical principles to interpret the calculator's output correctly. Blindly accepting the results without understanding the process can be detrimental to learning.
- Algorithmic Limitations: The algorithms used by different calculators might differ slightly, potentially leading to minute variations in results for borderline cases.
Advanced Tips for Effective Usage
- Multiple Checks: If possible, use multiple calculators or perform manual checks to verify the results.
- Understand the Underlying Math: A strong grasp of power series, convergence tests, and the radius of convergence is essential for effective usage.
- Start Simple: Begin with simpler examples to become comfortable with the calculator's interface and functionality before tackling complex problems.
- Explore Different Calculators: Different calculators might offer different features and capabilities; exploring several can broaden your understanding.
- Interpret Results Critically: Don't just accept the output; analyze the results in the context of the original power series and the applied tests.
Example: Using a Hypothetical Calculator
Let's consider the power series:
∑<sub>n=1</sub><sup>∞</sup> (x - 2)<sup>n</sup> / n
Using a hypothetical find the interval of convergence calculator, we'd input the coefficients (1/n) and the center (a = 2). The calculator would then:
- Apply the Ratio Test: It would compute the limit of the ratio of consecutive terms.
- Determine the Radius of Convergence: Based on the ratio test, it would find the radius of convergence (R).
- Check Endpoints: It would substitute x = 2 - R and x = 2 + R into the original series and apply appropriate convergence tests (likely the alternating series test for one endpoint and a p-series test for another).
- Output the Interval of Convergence: Finally, it would output the interval of convergence, specifying whether the endpoints are included or excluded. For this example, the correct interval of convergence is [1, 3), meaning the series converges at x = 1 and diverges at x = 3.
Conclusion
A find the interval of convergence calculator is a powerful tool for efficiently and accurately determining the interval of convergence of power series. However, its effective use requires a solid understanding of the underlying mathematical principles and a critical approach to interpreting the results. By combining the computational power of these calculators with a thorough understanding of the mathematics, students and professionals can significantly improve their ability to analyze and work with power series. Remember to always double-check your inputs and critically evaluate the output to ensure accuracy and a thorough understanding of the concepts. The calculator should serve as a tool to enhance your mathematical skills, not replace them.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Kilos Is 110 Lbs
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 163 Cm
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Percent Of 200 Is 10
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Miles Is 180 Kilometers
Mar 29, 2025
-
21 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Find The Interval Of Convergence Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
