Find The Area Of Shaded Region Calculator
Greels
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
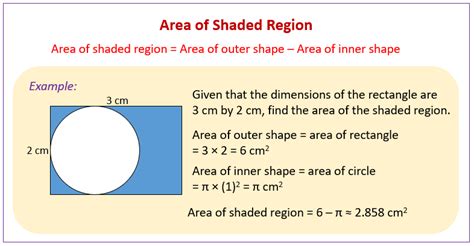
Table of Contents
Find the Area of a Shaded Region Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the area of a shaded region can be a tricky task, especially when dealing with complex shapes. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various methods for calculating shaded areas, exploring different geometric figures and providing you with a conceptual understanding, supplemented by practical examples. We'll also touch upon the use of online "find the area of shaded region calculator" tools to expedite the process. While no direct links to specific calculators will be provided to remain compliant with the instructions, understanding the underlying principles will allow you to effectively utilize any such tool you may find.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Geometric Shapes and Formulas
Before tackling shaded regions, it's crucial to have a solid grasp of the area formulas for common geometric shapes. These form the building blocks for calculating more complex areas.
1. Rectangle:
- Formula: Area = length × width
- Key points: A rectangle is a four-sided polygon with four right angles. The length and width must be perpendicular.
2. Square:
- Formula: Area = side × side = side²
- Key points: A square is a special type of rectangle where all four sides are equal in length.
3. Triangle:
- Formula: Area = (1/2) × base × height
- Key points: The base and height must be perpendicular. The height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex.
4. Circle:
- Formula: Area = π × radius²
- Key points: The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on the circumference. π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
5. Trapezoid:
- Formula: Area = (1/2) × (base1 + base2) × height
- Key points: A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides (the bases). The height is the perpendicular distance between the bases.
Calculating Shaded Regions: Strategies and Techniques
Calculating the area of a shaded region often involves subtracting the area of one or more shapes from the area of a larger shape. Let's examine some common scenarios and strategies.
1. Shaded Region within a Rectangle:
Imagine a rectangle with a smaller circle inscribed within it. To find the shaded area (the area of the rectangle excluding the circle), follow these steps:
- Calculate the area of the rectangle: Use the formula: Area = length × width.
- Calculate the area of the circle: Use the formula: Area = π × radius².
- Subtract the area of the circle from the area of the rectangle: Shaded Area = Area(Rectangle) - Area(Circle).
2. Overlapping Shapes:
When shapes overlap, the shaded region might represent the area of the overlap or the area of one shape minus the overlap. Let's consider two overlapping circles:
- Find the area of each circle individually.
- Calculate the area of the overlapping region. This often requires using geometry and trigonometry. Sometimes, approximations might be necessary.
- Depending on which area is shaded, either add or subtract the overlapping area. If the shaded region is the combined area of both circles, add the individual areas and subtract the overlapping area to avoid double-counting. If only the area outside the overlap is shaded, subtract the overlapping area from the sum of the individual areas.
3. Shaded Region involving Irregular Shapes:
For irregular shapes, breaking them down into smaller, manageable shapes is often the best approach. This might involve dividing the shape into rectangles, triangles, or other regular shapes. Calculate the area of each smaller shape and sum them up to find the total shaded area. This might require creative problem-solving and a keen eye for geometric relationships.
4. Using Coordinate Geometry:
If the shaded region is defined by coordinates on a Cartesian plane, you can utilize techniques from coordinate geometry. This could involve finding the area using integration techniques (calculus) or using determinant formulas for polygons defined by their vertices.
Utilizing "Find the Area of Shaded Region Calculator" Tools
Online calculators can significantly simplify the process, particularly for complex scenarios. While specific tools won't be linked here, when searching for such a calculator, keep the following in mind:
- Input Methods: Look for calculators that allow you to input data in various formats – dimensions directly, coordinates, or even by uploading an image.
- Shape Recognition: Some advanced calculators might use image recognition to automatically identify shapes and calculate areas.
- Step-by-Step Solutions: Calculators that show the steps involved are extremely valuable for learning and understanding the process.
- Multiple Shape Support: Choose calculators capable of handling various combinations of shapes.
Advanced Concepts and Challenges
While the above examples cover many common scenarios, some situations present unique challenges:
- Complex Overlaps: Determining the area of highly irregular or intricately overlapping shapes can be computationally intensive.
- Three-Dimensional Shaded Regions: Extending the concept to three dimensions involves calculating volumes, adding another layer of complexity.
- Applications in Calculus: More advanced methods, such as integral calculus, are necessary to handle shaded regions with curved boundaries.
Practical Examples
Let's work through a few illustrative examples to solidify our understanding.
Example 1: Square with Inscribed Circle:
A square with a side length of 10 cm has a circle inscribed within it. Find the area of the shaded region (the area of the square outside the circle).
- Area of the square: 10 cm × 10 cm = 100 cm²
- Radius of the circle: The diameter of the circle is equal to the side length of the square (10 cm), so the radius is 5 cm.
- Area of the circle: π × (5 cm)² ≈ 78.54 cm²
- Shaded area: 100 cm² - 78.54 cm² ≈ 21.46 cm²
Example 2: Overlapping Rectangles:
Two identical rectangles, each with a length of 8 cm and a width of 4 cm, overlap partially. The overlapping region is a smaller rectangle with dimensions 4 cm by 2 cm. Find the total shaded area (the area of both rectangles excluding the overlap).
- Area of one rectangle: 8 cm × 4 cm = 32 cm²
- Total area of both rectangles: 2 × 32 cm² = 64 cm²
- Area of the overlap: 4 cm × 2 cm = 8 cm²
- Shaded area: 64 cm² - 8 cm² = 56 cm²
Conclusion: Mastering Shaded Region Calculations
Finding the area of a shaded region is a fundamental skill in geometry and has practical applications in various fields. While simple cases involve straightforward calculations, more complex scenarios might require creative problem-solving, the use of appropriate formulas, and potentially the assistance of online calculators. By understanding the underlying geometric principles and employing systematic approaches, you can confidently tackle even the most challenging shaded region problems. Remember to break down complex shapes into simpler ones, carefully identify the relevant areas, and double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy. With practice and a methodical approach, mastering shaded area calculations will become second nature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
81 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Cm Is 35 Inches
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is 75 Inches In Feet
Mar 23, 2025
-
60 Pounds Is How Many Ounces
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Pounds Is 2 5 Kilograms
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Find The Area Of Shaded Region Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
