Find Area Under A Curve Calculator
Greels
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
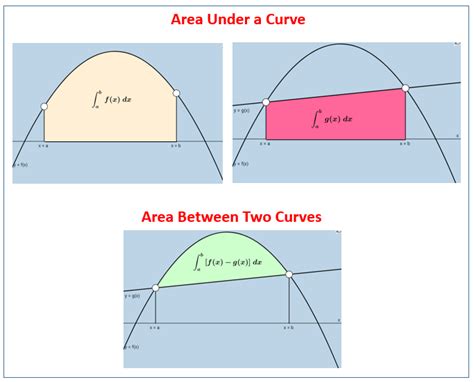
Table of Contents
Find Area Under a Curve Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the area under a curve is a fundamental concept in calculus with wide-ranging applications in various fields, from physics and engineering to economics and statistics. While manual calculation can be complex and time-consuming, especially for intricate functions, online "find area under a curve calculator" tools provide a convenient and efficient solution. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of area calculation, exploring different methods, their applications, and the crucial role of online calculators in simplifying the process.
Understanding the Concept: Area Under a Curve
The area under a curve represents the integral of a function over a specified interval. Imagine the curve as the top boundary of a region, and the x-axis as the bottom boundary. The area enclosed between these boundaries represents the accumulated value of the function across that interval. This area calculation provides crucial information about the function's behavior and its cumulative effect.
Why is Calculating the Area Under a Curve Important?
The significance of calculating the area under a curve extends far beyond theoretical mathematics. Here are some key applications:
- Physics: Determining the distance traveled by an object given its velocity function over time. The area under the velocity-time curve represents the total displacement.
- Engineering: Calculating the work done by a force, where the area under a force-displacement curve represents the total work performed.
- Economics: Determining the total cost or revenue over a given period, where the area under a cost/revenue function represents the accumulated amount.
- Probability and Statistics: Calculating probabilities using probability density functions. The area under the curve within a specific range represents the probability of the random variable falling within that range.
- Medicine: Analyzing drug concentration levels over time. The area under the curve (AUC) of the drug concentration-time graph is a crucial pharmacokinetic parameter.
Methods for Calculating Area Under a Curve
Several methods exist for calculating the area under a curve, ranging from simple geometric approximations to sophisticated numerical integration techniques.
1. Geometric Methods: Simple Shapes
For simple functions that result in geometric shapes (rectangles, triangles, trapezoids, etc.), the area can be calculated using basic geometric formulas. This method is straightforward but limited to functions that produce easily identifiable shapes.
Example: If the function is a straight line forming a triangle with the x-axis, the area is calculated using the formula: Area = (1/2) * base * height.
2. Numerical Integration Techniques
When dealing with complex functions where geometric methods are inapplicable, numerical integration techniques are employed. These methods approximate the area under the curve by dividing it into smaller segments and summing the areas of these segments. Common techniques include:
- Riemann Sums: This method approximates the area using rectangles, where the height of each rectangle is determined by the function's value at a specific point within the interval. There are left Riemann sums, right Riemann sums, and midpoint Riemann sums, each with its own level of accuracy.
- Trapezoidal Rule: This method approximates the area using trapezoids, providing a more accurate approximation than Riemann sums, especially for curved functions. The area of each trapezoid is calculated using the formula: Area = (1/2) * (base1 + base2) * height.
- Simpson's Rule: This method uses parabolic curves to approximate the function within each interval, leading to even greater accuracy than the trapezoidal rule, especially for smooth curves. This method requires an even number of intervals.
3. Analytical Integration (Calculus)
For functions with known antiderivatives, the area under the curve can be calculated analytically using the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. This involves finding the antiderivative of the function, evaluating it at the upper and lower limits of integration, and subtracting the results. This method provides the exact area, unlike numerical methods which provide approximations.
Example: To find the area under the curve of f(x) = x² from x=0 to x=2, one would find the antiderivative (F(x) = (1/3)x³), evaluate F(2) and F(0), and then subtract: F(2) - F(0) = (1/3)(2)³ - (1/3)(0)³ = 8/3.
The Role of Online "Find Area Under a Curve Calculator" Tools
Online area under the curve calculators streamline the calculation process, eliminating the need for manual computation, especially for complex functions or when high accuracy is required. These tools typically offer:
- Ease of Use: Users simply input the function and the integration limits. The calculator handles the complex calculations and provides the result instantly.
- Variety of Methods: Many calculators offer different numerical integration methods (Riemann sums, trapezoidal rule, Simpson's rule) allowing users to choose the most appropriate method based on the function's complexity and desired accuracy.
- Visualization: Some calculators provide graphical representations of the function and the shaded area, enhancing understanding and interpretation.
- Accuracy: Sophisticated calculators use advanced algorithms to achieve high accuracy, minimizing approximation errors inherent in numerical integration.
- Time Saving: Calculating the area under a curve manually can be time-consuming. Online calculators provide immediate results, boosting efficiency.
Choosing the Right Calculator and Method
The choice of calculator and integration method depends on several factors:
- Function Complexity: Simple functions might require only basic geometric calculations or simple Riemann sums. Complex functions necessitate more advanced numerical methods like the trapezoidal rule or Simpson's rule.
- Desired Accuracy: If high accuracy is crucial, Simpson's rule or analytical integration (if feasible) is preferable. For less demanding applications, simpler methods may suffice.
- Computational Resources: For very complex functions or extremely large intervals, computationally intensive numerical methods might require more powerful computing resources.
- User Familiarity: The ease of use and interface of the calculator are critical factors, especially for users with limited mathematical backgrounds.
Advanced Applications and Considerations
Beyond the basic applications discussed earlier, area under the curve calculations play a vital role in more advanced contexts:
- Fourier Analysis: Analyzing periodic functions and decomposing them into simpler sinusoidal components.
- Differential Equations: Solving differential equations numerically using techniques like the Runge-Kutta method, which often involve area under curve approximations.
- Machine Learning: Training models using numerical integration techniques for optimization and gradient calculations.
Conclusion
Calculating the area under a curve is a powerful tool with widespread applications across diverse disciplines. While manual calculation can be challenging, online "find area under a curve calculator" tools offer a user-friendly and efficient solution. By understanding the different methods and choosing the appropriate tool, users can effectively determine the area under a curve, unlocking valuable insights from complex functions and datasets. The availability of these online calculators has democratized access to this fundamental concept, making it readily accessible to students, researchers, and professionals alike. Remember to choose a calculator that meets your specific needs regarding accuracy, function complexity, and user-friendliness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Is 64 Cm
Mar 25, 2025
-
7 7c 1 4c 13 3c 2
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Kg Is 240 Lbs
Mar 25, 2025
-
90 Grams Is How Many Ounces
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is 41 Inches In Feet
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Find Area Under A Curve Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
