Express Your Answer As A Polynomial In Standard Form
Greels
Mar 19, 2025 · 4 min read
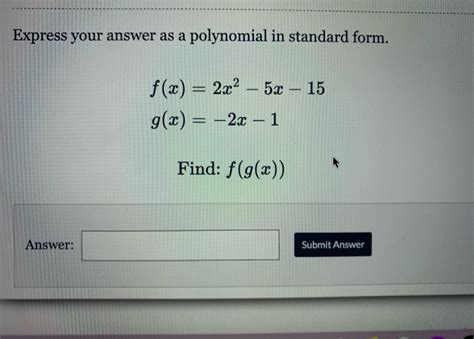
Table of Contents
Expressing Answers as Polynomials in Standard Form: A Comprehensive Guide
Polynomials are fundamental building blocks in algebra and beyond. Understanding how to express answers as polynomials in standard form is crucial for success in various mathematical disciplines, from solving equations to modeling real-world phenomena. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the concept, exploring its nuances and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding.
What is a Polynomial?
A polynomial is an expression consisting of variables (often represented by 'x'), coefficients, and exponents, combined using addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Crucially, the exponents of the variables must be non-negative integers. Terms in a polynomial are separated by addition or subtraction.
Examples of Polynomials:
- 3x² + 5x - 7
- 2x⁴ - x³ + 4x + 1
- x⁵ + 2
- 7 (This is a constant polynomial, a special case)
Examples that are NOT Polynomials:
- 2/x + 5 (Negative exponent)
- x^(1/2) + 3 (Fractional exponent)
- 1/(x + 2) (Variable in the denominator)
Standard Form of a Polynomial
The standard form of a polynomial arranges its terms in descending order of their exponents. For example, the polynomial 5x + x³ - 2 + 3x² would be written in standard form as:
x³ + 3x² + 5x - 2
The highest exponent is called the degree of the polynomial. In the example above, the degree is 3 (a cubic polynomial). The term with the highest exponent is called the leading term, and its coefficient is the leading coefficient (in this case, 1).
Operations on Polynomials and Standard Form
Understanding how to perform basic operations—addition, subtraction, multiplication—on polynomials is crucial for expressing results in standard form.
Adding Polynomials
To add polynomials, combine like terms (terms with the same variable and exponent). Then, arrange the terms in descending order of their exponents to express the result in standard form.
Example:
Add (2x² + 3x - 1) and (x² - 2x + 5):
(2x² + 3x - 1) + (x² - 2x + 5) = (2x² + x²) + (3x - 2x) + (-1 + 5) = 3x² + x + 4
Subtracting Polynomials
Subtracting polynomials is similar to addition, but remember to distribute the negative sign to all terms in the polynomial being subtracted. Then, combine like terms and arrange in descending order.
Example:
Subtract (x³ - 4x + 2) from (2x³ + x² - 3x + 1):
(2x³ + x² - 3x + 1) - (x³ - 4x + 2) = 2x³ + x² - 3x + 1 - x³ + 4x - 2 = x³ + x² + x - 1
Multiplying Polynomials
Multiplying polynomials requires the distributive property (often referred to as FOIL for binomials). Multiply each term in the first polynomial by each term in the second polynomial. Then, combine like terms and arrange in standard form.
Example:
Multiply (2x + 3) and (x² - x + 1):
(2x + 3)(x² - x + 1) = 2x(x² - x + 1) + 3(x² - x + 1) = 2x³ - 2x² + 2x + 3x² - 3x + 3 = 2x³ + x² - x + 3
Advanced Techniques and Applications
The standard form of polynomials isn't just a matter of neat organization; it plays a vital role in several advanced concepts.
Polynomial Division
Polynomial long division and synthetic division are techniques used to divide one polynomial by another. The result is expressed as a quotient and a remainder, both of which are polynomials. The standard form is crucial for systematically performing these divisions.
Finding Roots and Factors
The standard form assists in finding the roots (solutions) of polynomial equations. For example, the Rational Root Theorem helps narrow down potential rational roots based on the coefficients of the polynomial in standard form. Factoring polynomials, which often involves finding roots, is made easier with the polynomial in standard form.
Graphing Polynomials
The standard form of a polynomial provides valuable insights into its graph. The leading term dictates the end behavior of the graph (how the graph behaves as x approaches positive or negative infinity). The degree and leading coefficient together determine whether the graph rises or falls at both ends.
Applications in Calculus
In calculus, derivatives and integrals of polynomials are easily computed. Expressing the polynomial in standard form simplifies these calculations considerably.
Real-world Applications
Polynomials are not just theoretical constructs; they find extensive applications in various fields:
- Physics: Modeling projectile motion, oscillations, and other physical phenomena often involves polynomials.
- Engineering: Designing curves for roads, bridges, and other structures uses polynomial approximations.
- Economics: Analyzing economic trends and forecasting often involves polynomial regression.
- Computer Graphics: Creating smooth curves and surfaces in computer graphics relies heavily on polynomials (Bezier curves, for example).
Practice Problems
To solidify your understanding, try these practice problems:
- Express the polynomial 4x - 2x³ + 5 + x² in standard form.
- Add the polynomials (3x⁴ - 2x² + 1) and (x⁴ + 5x² - 3x + 2).
- Subtract (2x³ - x + 4) from (5x³ + 2x² - 3).
- Multiply (x - 2) and (x² + 3x - 1).
- Determine the degree and leading coefficient of the polynomial 7x⁵ - 2x² + x - 9.
Conclusion
Expressing answers as polynomials in standard form is more than a mere formatting convention; it's a fundamental skill that underpins various mathematical operations and real-world applications. Mastering this skill unlocks deeper understanding in algebra, calculus, and other related fields, enabling you to tackle increasingly complex problems and models effectively. Consistent practice and a solid grasp of polynomial operations are key to proficiency. Remember to always check your work by expanding your answers and confirming they are equivalent to the original expressions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 200 Meters
Mar 20, 2025
-
General Form To Conic Form Calculator
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Miles In 400 Km
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Miles In 70 Km
Mar 20, 2025
-
Adding And Subtracting Rational Expressions Calculator With Steps
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Express Your Answer As A Polynomial In Standard Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
