Derivative Of Cos 2 X 2
Greels
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
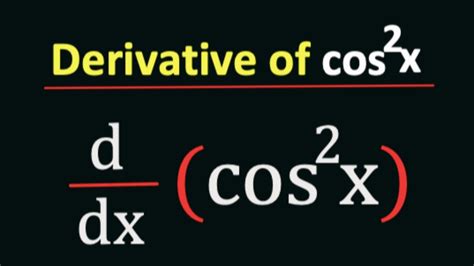
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Derivative of cos(2x²): A Comprehensive Guide
The derivative of a function describes its instantaneous rate of change at any given point. Understanding how to find derivatives is fundamental in calculus and has wide-ranging applications in various fields, from physics and engineering to economics and finance. This article delves into the process of finding the derivative of cos(2x²), exploring the underlying concepts and techniques involved. We will break down the problem step-by-step, addressing potential challenges and offering insights for a deeper understanding.
Understanding the Chain Rule: The Key to Solving Complex Derivatives
Before tackling the derivative of cos(2x²), it's crucial to grasp the chain rule. This powerful rule allows us to differentiate composite functions – functions within functions. The chain rule states that the derivative of a composite function is the derivative of the outer function (with the inside function left alone) multiplied by the derivative of the inner function. Mathematically, this can be represented as:
d/dx [f(g(x))] = f'(g(x)) * g'(x)
Where:
- f(x) is the outer function
- g(x) is the inner function
- f'(x) is the derivative of the outer function
- g'(x) is the derivative of the inner function
In our case, cos(2x²) is a composite function:
- Outer function: f(x) = cos(x)
- Inner function: g(x) = 2x²
Step-by-Step Differentiation of cos(2x²)
Now, let's apply the chain rule to find the derivative of cos(2x²):
-
Differentiate the outer function: The derivative of cos(x) is -sin(x). So, f'(x) = -sin(x).
-
Substitute the inner function: Replace 'x' in f'(x) with the inner function g(x) = 2x². This gives us -sin(2x²).
-
Differentiate the inner function: The derivative of 2x² is found using the power rule: d/dx (axⁿ) = naxⁿ⁻¹. Applying this, we get g'(x) = 4x.
-
Multiply the results: Finally, multiply the derivative of the outer function (with the inner function substituted) by the derivative of the inner function:
d/dx [cos(2x²)] = -sin(2x²) * 4x = -4x sin(2x²)
Therefore, the derivative of cos(2x²) is -4x sin(2x²).
Visualizing the Derivative: Graphical Interpretation
Understanding the derivative graphically provides a valuable visual aid. The derivative of a function represents the slope of the tangent line at any point on the function's graph. The graph of y = cos(2x²) is a periodic function with a rapidly oscillating nature due to the 2x² term. Its derivative, -4x sin(2x²), will also oscillate, but its amplitude will change depending on the value of x. For larger values of x, the amplitude of the oscillations will increase. The sign of the derivative indicates whether the original function is increasing or decreasing at that point. A positive derivative indicates an increasing function, while a negative derivative indicates a decreasing function.
Applications of the Derivative: Real-World Examples
The derivative of cos(2x²) and similar trigonometric functions have widespread applications in various scientific and engineering fields. Here are some examples:
-
Physics: In oscillatory motion (like a pendulum or a spring-mass system), trigonometric functions are frequently used to model the displacement, velocity, and acceleration of the object. The derivative allows us to determine the velocity and acceleration from the displacement function.
-
Engineering: In signal processing, trigonometric functions represent signals. The derivative can be used to analyze the rate of change of signals and perform filtering operations.
-
Economics: In financial modeling, derivatives are crucial for understanding and managing risk. For example, the derivative can be used to determine the rate of change of the value of an asset over time.
Advanced Techniques: Exploring Beyond the Basics
While the chain rule effectively solves the derivative of cos(2x²), let's explore some additional techniques that enhance our understanding and can be applied to more complex scenarios:
-
Implicit Differentiation: This technique is useful when dealing with equations that cannot be easily solved for y in terms of x. It involves differentiating both sides of the equation with respect to x, treating y as a function of x.
-
Logarithmic Differentiation: This method simplifies the differentiation of complex functions by taking the natural logarithm of both sides before differentiating. It is particularly helpful when dealing with functions involving products, quotients, and exponents.
-
Higher-Order Derivatives: Finding the second, third, and higher-order derivatives involves successively differentiating the function. The second derivative represents the rate of change of the rate of change (e.g., acceleration in physics).
Error Analysis and Potential Pitfalls
When calculating derivatives, it's crucial to be meticulous to avoid common errors:
-
Incorrect application of the chain rule: Carefully identify the inner and outer functions and apply the chain rule correctly.
-
Algebraic mistakes: Double-check your algebraic manipulations throughout the process.
-
Sign errors: Pay close attention to negative signs, especially when dealing with trigonometric functions.
-
Confusion with trigonometric identities: Ensure your understanding of trigonometric identities is strong to simplify expressions.
Expanding Your Knowledge: Further Exploration
To further solidify your understanding of derivatives and their applications, consider these avenues for exploration:
-
Practice problems: Work through various problems involving different types of functions and apply the relevant differentiation techniques.
-
Online resources: Numerous online resources, including interactive tutorials and practice exercises, can help you reinforce your learning.
-
Textbooks: Comprehensive calculus textbooks offer detailed explanations and a wealth of examples.
-
Advanced calculus topics: Explore advanced topics such as partial derivatives (for multivariable functions) and differential equations, building upon your foundation in basic differentiation.
Conclusion: Mastering the Derivative of cos(2x²) and Beyond
Finding the derivative of cos(2x²) is a fundamental exercise that illustrates the power and versatility of the chain rule in calculus. By understanding this process, and the broader concepts of differentiation, you’ve taken a significant step in mastering a core element of calculus. This knowledge serves as a building block for more advanced mathematical concepts and has wide-reaching applications across numerous disciplines. Remember, practice is key, and consistent effort will solidify your understanding and empower you to tackle more complex derivatives with confidence.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 97 Fahrenheit In Celsius
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Kg In 25 Pounds
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is 12 Percent Of 15
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 76 Inches
Mar 19, 2025
-
48 Oz Is How Many Ml
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Derivative Of Cos 2 X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
