Critical Numbers Of A Function Calculator
Greels
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
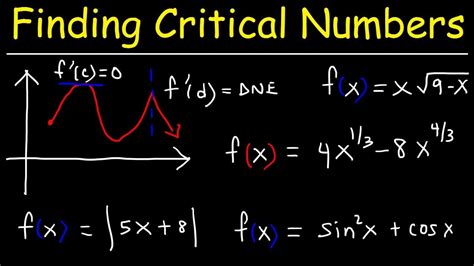
Table of Contents
Critical Numbers of a Function Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding critical numbers of a function is a crucial step in calculus, particularly when analyzing the behavior of a function, such as identifying local maxima and minima, inflection points, and intervals of increase or decrease. While the process is straightforward, it can be time-consuming and prone to errors, especially with complex functions. This is where a critical numbers of a function calculator becomes invaluable. This article will explore the concept of critical numbers, detail the steps involved in calculating them manually, and discuss the advantages of using a critical numbers calculator, along with important considerations and applications.
Understanding Critical Numbers
A critical number of a function f(x) is a value x in the domain of f where either the derivative f'(x) is zero or f'(x) is undefined. These points are significant because they represent potential locations of local extrema (maximum or minimum values) within the function's graph. It's crucial to remember that a critical number is not necessarily a local extremum; it's simply a point where the function's behavior changes significantly.
Key aspects to remember about critical numbers:
- Derivative is zero (f'(x) = 0): This indicates a horizontal tangent line at the point, suggesting a potential local maximum or minimum.
- Derivative is undefined (f'(x) is undefined): This occurs at points where the function is not differentiable, such as sharp corners (cusps), vertical tangents, or points of discontinuity. These points can also be locations of extrema or other significant changes in behavior.
- Domain Restriction: Critical numbers must lie within the function's domain. Points outside the domain, even if they satisfy f'(x) = 0 or f'(x) is undefined, are not considered critical numbers.
Calculating Critical Numbers Manually: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating critical numbers manually requires a systematic approach:
-
Find the Derivative: The first step is to find the first derivative, f'(x), of the function f(x). This often involves applying rules of differentiation such as the power rule, product rule, quotient rule, or chain rule, depending on the complexity of the function.
-
Set the Derivative to Zero: Solve the equation f'(x) = 0 for x. This will give you the x-values where the derivative is zero. These are potential critical numbers.
-
Find Where the Derivative is Undefined: Identify any points where the derivative f'(x) is undefined. This usually happens at points where the function has:
- Vertical asymptotes: The function approaches infinity or negative infinity.
- Sharp corners or cusps: The function's slope changes abruptly.
- Points of discontinuity: The function has a "break" or jump in its graph.
-
Check for Domain Restrictions: Ensure that all the x-values obtained in steps 2 and 3 are within the domain of the original function f(x). Any values outside the domain are discarded.
-
Identify Critical Numbers: The x-values that satisfy steps 2, 3, and 4 are the critical numbers of the function.
Example:
Let's consider the function f(x) = x³ - 3x + 2.
-
Find the Derivative: f'(x) = 3x² - 3
-
Set the Derivative to Zero: 3x² - 3 = 0 => x² = 1 => x = ±1
-
Find Where the Derivative is Undefined: The derivative f'(x) = 3x² - 3 is a polynomial and is defined for all real numbers. Therefore, there are no points where the derivative is undefined.
-
Check for Domain Restrictions: The function f(x) = x³ - 3x + 2 is a polynomial and its domain is all real numbers.
-
Identify Critical Numbers: The critical numbers are x = 1 and x = -1.
The Advantages of Using a Critical Numbers of a Function Calculator
While manual calculation is valuable for understanding the underlying concepts, using a critical numbers calculator offers several significant advantages:
-
Speed and Efficiency: Calculators can quickly determine critical numbers, saving considerable time, especially with complex functions. This is particularly helpful when dealing with numerous functions or when time is a constraint.
-
Accuracy: Manual calculations are prone to errors, especially with intricate derivatives or equations. Calculators minimize this risk, providing accurate results consistently.
-
Handling Complex Functions: Calculators can effortlessly handle functions that are difficult or impossible to solve manually, such as those involving transcendental functions (trigonometric, exponential, logarithmic).
-
Visualization: Many calculators provide graphical representations of the function and its derivative, allowing for a better visual understanding of the critical points and their relationship to the function's overall behavior. This visual aid enhances comprehension and allows for verification of the calculated critical numbers.
Choosing and Using a Critical Numbers Calculator
The best calculator for your needs will depend on your specific requirements and the complexity of the functions you are working with. Look for calculators that:
-
Support a wide range of functions: The calculator should be able to handle various types of functions, including polynomials, rational functions, trigonometric functions, exponential functions, and logarithmic functions.
-
Provide step-by-step solutions: This is beneficial for learning and understanding the underlying process.
-
Offer clear and concise results: The output should be easy to interpret and understand.
-
Have a user-friendly interface: The calculator should be intuitive and easy to navigate.
Applications of Critical Numbers
Understanding and finding critical numbers has wide-ranging applications in various fields:
-
Optimization Problems: In engineering, economics, and operations research, critical numbers are crucial for finding maximum or minimum values, which represent optimal solutions to problems involving maximizing profit, minimizing cost, or optimizing resource allocation.
-
Curve Sketching: Critical numbers help determine the intervals where a function is increasing or decreasing, the location of local maxima and minima, and the concavity of the curve, enabling the accurate sketching of the function's graph.
-
Physics and Engineering: Critical points are used extensively in physics and engineering to analyze the behavior of systems, such as determining equilibrium points, stability analysis, and modeling physical phenomena.
-
Machine Learning and Data Science: In optimization algorithms used in machine learning, critical numbers play a vital role in finding optimal parameters for models, leading to improved accuracy and performance.
Beyond Critical Numbers: Second Derivative Test and Inflection Points
While critical numbers identify potential extrema, the second derivative test helps classify these points as local maxima, minima, or neither. The second derivative f''(x) evaluated at a critical number x provides this information:
- f''(x) > 0: The function is concave up at the critical number, indicating a local minimum.
- f''(x) < 0: The function is concave down at the critical number, indicating a local maximum.
- f''(x) = 0: The test is inconclusive; further analysis is required.
Additionally, inflection points, where the concavity of the function changes, occur when the second derivative is zero or undefined. These points represent significant changes in the function's curvature and are also important for comprehensive function analysis. Many advanced calculators can help determine inflection points along with critical numbers.
Conclusion
Critical numbers are fundamental to understanding the behavior of functions. While manual calculation is valuable for conceptual understanding, utilizing a critical numbers calculator offers significant advantages in terms of speed, accuracy, and the ability to handle complex functions. By combining manual understanding with the power of computational tools, you can efficiently analyze functions and solve various problems across diverse fields. Remember to always consider the function's domain and the implications of the second derivative test to obtain a complete and accurate analysis. Mastering the art of finding and interpreting critical numbers is a crucial skill for anyone working with calculus and its various applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
System Of Linear Equations Calculator Matrix
Mar 25, 2025
-
Cross Product Of 3 Vectors Calculator
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 58 Mm
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is 93 Days From Today
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Much Is 170 In Kilograms
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Critical Numbers Of A Function Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
