Cartesian Equation To Polar Equation Calculator
Greels
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
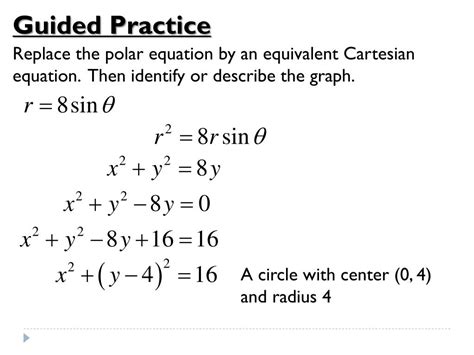
Table of Contents
Cartesian Equation to Polar Equation Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting between Cartesian (rectangular) and polar coordinate systems is a fundamental skill in mathematics, particularly in calculus, trigonometry, and physics. While the conversion process is relatively straightforward, manually converting complex equations can be time-consuming and prone to errors. This is where a Cartesian equation to polar equation calculator becomes invaluable. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of these coordinate systems, the conversion process, the benefits of using a calculator, and provides practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Cartesian and Polar Coordinate Systems
Before diving into the conversion process, let's review the fundamentals of each coordinate system:
Cartesian Coordinates (Rectangular Coordinates)
The Cartesian coordinate system, named after René Descartes, uses two perpendicular axes, typically labeled x and y, to uniquely identify any point in a two-dimensional plane. A point is represented by an ordered pair (x, y), where x represents the horizontal distance from the origin (0, 0) and y represents the vertical distance.
Key characteristics:
- Two perpendicular axes: x-axis (horizontal) and y-axis (vertical)
- Ordered pair (x, y): Represents the horizontal and vertical distances from the origin.
- Simple representation for lines and other simple shapes: Linear equations are easily represented.
Polar Coordinates
The polar coordinate system uses a distance and an angle to represent a point. A point is represented by an ordered pair (r, θ), where:
- r: Represents the radial distance from the origin (pole) to the point. It's always non-negative.
- θ: Represents the angle (in radians or degrees) measured counter-clockwise from the positive x-axis to the line segment connecting the origin and the point.
Key characteristics:
- Radial distance (r): Distance from the origin.
- Angle (θ): Angle from the positive x-axis.
- Circular symmetry: Equations often have simpler forms in polar coordinates than in Cartesian coordinates, especially those representing circles and other radially symmetric shapes.
The Conversion Process: Cartesian to Polar
The conversion from Cartesian to polar coordinates involves applying trigonometric relationships:
-
r = √(x² + y²) This formula calculates the distance from the origin using the Pythagorean theorem.
-
θ = tan⁻¹(y/x) This formula calculates the angle using the arctangent function. However, it's crucial to consider the quadrant of the point (x, y) to ensure the correct angle is obtained. The
arctanfunction typically only returns angles in the range (-π/2, π/2), so adjustments are needed for points in quadrants II and III.
The Conversion Process: Polar to Cartesian
The reverse conversion, from polar to Cartesian, is equally important and simpler:
-
x = r * cos(θ) The x-coordinate is obtained by projecting the radial distance onto the x-axis.
-
y = r * sin(θ) The y-coordinate is obtained by projecting the radial distance onto the y-axis.
Why Use a Cartesian Equation to Polar Equation Calculator?
While the conversion formulas are relatively straightforward, manually converting equations, especially those that are complex or involve multiple variables, can be error-prone and time-consuming. A Cartesian equation to polar equation calculator offers several advantages:
- Accuracy: Eliminates human errors in calculations.
- Efficiency: Saves time and effort, especially for complex equations.
- Ease of use: Calculators provide a user-friendly interface for inputting equations and obtaining results.
- Educational tool: Can be used as a learning aid to check answers and build understanding.
- Versatility: Many calculators can handle various types of equations and offer options for specifying the angle units (radians or degrees).
Practical Examples Using a Cartesian Equation to Polar Equation Calculator
Let's illustrate the conversion process with a few examples, highlighting the use of a calculator.
Example 1: Converting a Simple Equation
Consider the Cartesian equation: x² + y² = 4. This represents a circle with radius 2 centered at the origin. Using a Cartesian to polar calculator, you would input this equation. The calculator would utilize the relationships r² = x² + y² and automatically output the equivalent polar equation: r = 2. This elegantly shows the simplicity of representing circles in polar coordinates.
Example 2: Converting a More Complex Equation
Consider the Cartesian equation: x² - y² = 1. This equation represents a hyperbola. Inputting this equation into a polar equation calculator would yield a polar equation that would likely involve both 'r' and 'θ', showcasing how even relatively simple Cartesian equations can result in more intricate polar counterparts. The exact output will vary slightly depending on the specific calculator used but will be an equivalent representation of the hyperbola.
Example 3: Handling Equations with Trigonometric Functions
Consider a Cartesian equation involving trigonometric functions, for instance, x = cos(y). A Cartesian to polar equation calculator would simplify this equation by applying trigonometric identities and the conversion formulas mentioned earlier. The resultant polar equation would likely be a function of 'r' and 'θ', demonstrating the calculator's ability to handle equations of greater complexity.
Choosing a Cartesian Equation to Polar Equation Calculator
When choosing a calculator, consider the following features:
- Ease of use: The interface should be intuitive and easy to navigate.
- Accuracy: The calculator should provide accurate results.
- Support for various equation types: The calculator should be able to handle various types of equations, including those with trigonometric functions.
- Output format: The calculator should present the results in a clear and understandable format.
- Additional functionalities: Some calculators may offer additional features, such as graphing capabilities or the ability to convert between other coordinate systems.
Advanced Applications and Considerations
The conversion between Cartesian and polar coordinates has numerous applications beyond simple geometric problems. It plays a vital role in various fields:
- Physics: Describing the motion of particles in two dimensions.
- Engineering: Designing and analyzing systems with radial symmetry.
- Computer graphics: Representing and manipulating images and shapes.
- Signal processing: Analyzing and manipulating signals with circular symmetry.
Understanding the nuances of each coordinate system and the conversion process between them empowers you to tackle a broader range of mathematical and scientific challenges efficiently. The use of a suitable Cartesian equation to polar equation calculator is a significant tool in enhancing this understanding and simplifying the task of conversion, ensuring accuracy and saving valuable time. By selecting a reliable and versatile calculator and understanding its capabilities, you can unlock significant benefits across various applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
225 Kg Is How Many Pounds
Mar 20, 2025
-
308 Kilometers To Miles Per Hour
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Meters In 120 Feet
Mar 20, 2025
-
39 Kilos Is How Many Pounds
Mar 20, 2025
-
99 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cartesian Equation To Polar Equation Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
