Cartesian Coordinates To Polar Coordinates Calculator
Greels
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
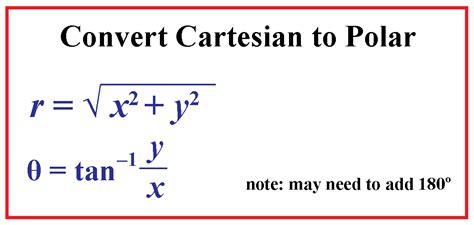
Table of Contents
- Cartesian Coordinates To Polar Coordinates Calculator
- Table of Contents
- Cartesian Coordinates to Polar Coordinates Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Cartesian and Polar Coordinates
- Cartesian Coordinates (Rectangular Coordinates)
- Polar Coordinates
- The Conversion Formulas
- From Cartesian to Polar Coordinates
- From Polar to Cartesian Coordinates
- The Role of a Cartesian to Polar Coordinates Calculator
- Applications of Coordinate System Conversions
- 1. Physics and Engineering
- 2. Computer Graphics and Game Development
- 3. Mathematics and Data Analysis
- 4. Navigation and Surveying
- Choosing and Using a Cartesian to Polar Coordinates Calculator
- Beyond Basic Conversion: Advanced Applications
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Cartesian Coordinates to Polar Coordinates Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting between Cartesian (rectangular) and polar coordinate systems is a fundamental concept in mathematics and numerous scientific and engineering fields. While the conversion formulas are straightforward, the process can be tedious, especially when dealing with numerous conversions or complex calculations. This is where a Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates calculator becomes invaluable. This article will delve into the intricacies of this conversion, explore the applications of these coordinate systems, and provide a comprehensive understanding of how a calculator streamlines the process.
Understanding Cartesian and Polar Coordinates
Before diving into the mechanics of conversion, let's solidify our understanding of the two coordinate systems.
Cartesian Coordinates (Rectangular Coordinates)
Cartesian coordinates, also known as rectangular coordinates, represent a point in a two-dimensional plane using two perpendicular axes: the x-axis (horizontal) and the y-axis (vertical). A point is uniquely identified by its x and y coordinates, written as an ordered pair (x, y). The x-coordinate represents the horizontal distance from the origin (0, 0), and the y-coordinate represents the vertical distance from the origin.
Example: The point (3, 4) is located 3 units to the right of the origin along the x-axis and 4 units above the origin along the y-axis.
Polar Coordinates
Polar coordinates represent a point in a plane using a distance (r) from the origin and an angle (θ) measured counter-clockwise from the positive x-axis. A point is represented as an ordered pair (r, θ). 'r' is always non-negative and represents the radial distance, while 'θ' (theta) represents the polar angle, typically expressed in radians or degrees.
Example: The point (5, 36.87°) is located 5 units from the origin at an angle of 36.87° counter-clockwise from the positive x-axis.
The Conversion Formulas
The conversion between Cartesian and polar coordinates involves simple trigonometric relationships.
From Cartesian to Polar Coordinates
-
r = √(x² + y²): The radial distance (r) is calculated using the Pythagorean theorem. It's the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle formed by the x and y coordinates.
-
θ = arctan(y/x): The polar angle (θ) is determined using the arctangent function. However, it's crucial to consider the quadrant of the point (x, y) to ensure the correct angle is obtained. The
arctanfunction typically returns an angle between -π/2 and π/2 radians (-90° and 90°). Therefore, adjustments are needed depending on the quadrant:- Quadrant I (x > 0, y > 0): θ = arctan(y/x)
- Quadrant II (x < 0, y > 0): θ = arctan(y/x) + π (or 180°)
- Quadrant III (x < 0, y < 0): θ = arctan(y/x) + π (or 180°)
- Quadrant IV (x > 0, y < 0): θ = arctan(y/x) + 2π (or 360°)
If x = 0, θ = π/2 (90°) if y > 0 and θ = 3π/2 (270°) if y < 0.
From Polar to Cartesian Coordinates
-
x = r * cos(θ): The x-coordinate is obtained by multiplying the radial distance (r) by the cosine of the polar angle (θ).
-
y = r * sin(θ): The y-coordinate is obtained by multiplying the radial distance (r) by the sine of the polar angle (θ).
The Role of a Cartesian to Polar Coordinates Calculator
Manually performing these calculations, especially for numerous points or complex angles, can be time-consuming and prone to errors. A Cartesian to polar coordinates calculator automates this process, providing accurate results quickly and efficiently.
Key benefits of using a calculator:
- Speed and Efficiency: Calculators perform conversions instantly, saving significant time compared to manual calculations.
- Accuracy: Eliminates the risk of human error in calculations, ensuring precise results.
- Ease of Use: Most calculators offer user-friendly interfaces, making them accessible even to users without a strong mathematical background.
- Handling of Different Units: Many calculators allow input of angles in both radians and degrees, providing flexibility.
- Batch Processing: Some advanced calculators might even allow for the conversion of multiple coordinate pairs simultaneously.
Applications of Coordinate System Conversions
The ability to convert between Cartesian and polar coordinates is crucial in various fields:
1. Physics and Engineering
- Projectile Motion: Analyzing the trajectory of projectiles often involves switching between coordinate systems to simplify calculations.
- Robotics: Robot arm movements and positioning are often described using polar coordinates, requiring conversion to Cartesian coordinates for precise control.
- Signal Processing: Representing signals in polar coordinates (amplitude and phase) can be advantageous for certain analyses.
- Fluid Dynamics: Describing fluid flow patterns often benefits from using polar coordinates.
2. Computer Graphics and Game Development
- Game Physics Engines: Many game engines use polar coordinates for representing object positions and rotations.
- Image Processing: Converting between coordinate systems is essential for image transformations and manipulations.
- Pathfinding Algorithms: Some pathfinding algorithms utilize polar coordinates for efficient navigation calculations.
3. Mathematics and Data Analysis
- Complex Numbers: Representing complex numbers in polar form (magnitude and argument) simplifies certain operations.
- Fourier Analysis: This technique extensively uses polar coordinates for analyzing periodic signals.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Converting between coordinate systems is crucial for integrating data from various sources.
4. Navigation and Surveying
- GPS Systems: GPS coordinates are often represented in geographic (latitude and longitude) which are essentially a spherical coordinate system, requiring conversion for various applications.
- Radar Systems: Radar data is often expressed in polar coordinates, needing conversion for display and analysis on Cartesian maps.
Choosing and Using a Cartesian to Polar Coordinates Calculator
When selecting a calculator, consider the following:
- Accuracy: Ensure the calculator uses precise algorithms to minimize errors.
- Interface: Choose a calculator with a user-friendly and intuitive interface.
- Functionality: Look for features like handling different angle units (radians and degrees) and the ability to handle multiple inputs.
- Availability: Consider whether you need an online calculator or a downloadable application.
Beyond Basic Conversion: Advanced Applications
While basic conversion is straightforward, advanced applications often involve:
- Three-Dimensional Conversions: Extending the concept to three dimensions (cylindrical and spherical coordinates) requires additional formulas and a more sophisticated calculator.
- Coordinate Transformations: Converting between different coordinate systems (e.g., Cartesian to cylindrical to spherical) involves chained conversions.
- Integration and Differentiation in Polar Coordinates: Applying calculus techniques in polar coordinates necessitates understanding the Jacobian determinant for coordinate transformations.
Conclusion
A Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates calculator is an invaluable tool for anyone working with these coordinate systems. Its ability to quickly and accurately perform conversions significantly simplifies calculations and reduces the risk of errors, freeing up time and resources for more complex analyses. Understanding the underlying principles of coordinate conversion and selecting the right calculator are crucial steps in leveraging its power across various disciplines. By mastering this fundamental mathematical operation and utilizing the appropriate technology, you'll significantly enhance your problem-solving capabilities and efficiency in numerous fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Kilograms In 45 Pounds
Mar 28, 2025
-
Expressing A Function As A Composition Of Two Functions Calculator
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Pounds In 43 Kg
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Oz Is 140 Grams
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 210 Cm
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cartesian Coordinates To Polar Coordinates Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
