Area Of Surface Of Revolution Calculator
Greels
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
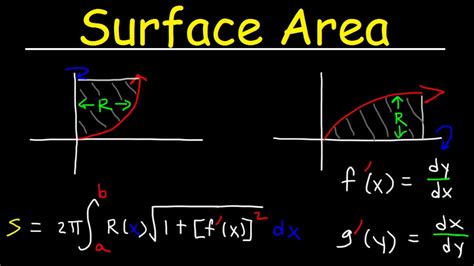
Table of Contents
Area of Surface of Revolution Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Calculating the surface area of a solid of revolution can be a complex mathematical undertaking. However, with the right tools and understanding, this process becomes significantly more manageable. This article provides a deep dive into the concept of surface area of revolution, explores different methods of calculation, and examines the utility of online calculators designed for this purpose. We'll cover everything from the fundamental mathematical principles to practical applications and troubleshooting common issues.
Understanding the Surface Area of Revolution
A surface of revolution is a surface generated by rotating a curve around an axis. Imagine taking a line or a more complex curve and spinning it around a central axis—the area this creates is the surface of revolution. The calculation of this area is crucial in various fields, including engineering, physics, and architecture, where understanding the surface area is essential for determining things like material requirements, heat transfer, and fluid dynamics.
Key Concepts and Terminology
Before delving into the calculations, let's clarify some essential terms:
-
Curve: The original curve that's being rotated. This can be defined by a function y = f(x), where 'y' is a function of 'x', or parametrically.
-
Axis of Revolution: The line around which the curve is rotated. This is typically the x-axis or y-axis, but it can be any line.
-
Surface of Revolution: The three-dimensional surface generated by rotating the curve around the axis.
-
Infinitesimal Strip: To calculate the total surface area, we break the curve into infinitely small segments. Each segment generates a thin, cylindrical strip when rotated. The area of this strip is approximated and summed to find the total surface area.
Methods for Calculating Surface Area of Revolution
Several methods exist for calculating the surface area of revolution. The most common involves integration.
Method 1: Using Integration (for functions of x)
If the curve is defined by a function y = f(x) and is rotated around the x-axis, the surface area (S) is given by the following integral:
S = 2π ∫<sub>a</sub><sup>b</sup> y √(1 + (dy/dx)²) dx
Where:
aandbare the limits of integration (the x-coordinates defining the portion of the curve being rotated).y = f(x)is the function defining the curve.dy/dxis the derivative of the function with respect to x.
This formula stems from considering an infinitesimal strip, approximating its area as a rectangle with length 2πy (the circumference of a circle with radius y) and width √(1 + (dy/dx)²)dx (using the Pythagorean theorem to account for the curve's slope).
Example: Find the surface area of the curve y = x² from x = 0 to x = 1 rotated around the x-axis.
-
Find dy/dx: dy/dx = 2x
-
Substitute into the formula: S = 2π ∫<sub>0</sub><sup>1</sup> x² √(1 + (2x)²) dx
-
Solve the integral (this often requires substitution techniques): This integral is solvable, but it leads to a somewhat complex calculation involving trigonometric substitution.
Method 2: Using Integration (for parametric equations)
When the curve is defined parametrically (x = g(t), y = h(t)), the formula becomes:
S = 2π ∫<sub>α</sub><sup>β</sup> y √((dx/dt)² + (dy/dt)²) dt
Where:
- α and β are the parameter limits.
- dx/dt and dy/dt are the derivatives of x and y with respect to the parameter t.
Method 3: Numerical Integration
For complex curves where finding an analytical solution to the integral is difficult or impossible, numerical integration methods are used. These methods approximate the integral using numerical techniques such as:
-
Trapezoidal Rule: Approximates the area under the curve using trapezoids.
-
Simpson's Rule: Uses parabolas to approximate the area, providing a more accurate result.
-
Gaussian Quadrature: A more advanced method that uses strategically chosen points to achieve high accuracy.
Numerical integration is commonly implemented using software or online calculators.
The Role of an Area of Surface of Revolution Calculator
Online calculators provide a significant advantage in calculating the surface area of revolution. They automate the complex integration process, reducing the risk of errors and saving significant time. These calculators often handle both functions of x and parametric equations, and many incorporate numerical integration methods for complex scenarios.
Benefits of Using a Calculator
-
Speed and Efficiency: Calculators instantly provide results, eliminating the time-consuming manual calculations.
-
Accuracy: Reduces the likelihood of mathematical errors inherent in manual integration.
-
Handling Complex Functions: Easily handles functions that would be difficult or impossible to integrate manually.
-
Accessibility: Makes this powerful mathematical tool accessible to a wider audience, even those without advanced mathematical skills.
Features to Look for in a Good Calculator
A robust surface area of revolution calculator should:
-
Support various input methods: Accept functions defined explicitly (y = f(x)), parametrically (x = g(t), y = h(t)), or even through data points.
-
Provide clear and detailed output: Show not just the final result but also the intermediate steps, if possible, for better understanding.
-
Handle different axes of revolution: Allow rotation around the x-axis, y-axis, or other specified axes.
-
Implement various integration techniques: Offer both analytical and numerical integration methods to handle diverse problems.
-
User-friendly interface: Have an intuitive interface that is easy to navigate and use.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with a calculator, challenges can arise. Here are some common issues and solutions:
-
Incorrect Function Input: Double-check your function's syntax and ensure it's correctly entered into the calculator.
-
Integration Limits: Carefully define the limits of integration to cover the desired portion of the curve.
-
Choosing the Right Integration Method: If an analytical solution fails, try a numerical method.
-
Handling Singularities: Some functions may have points where the derivative is undefined (singularities). These require special handling, often involving splitting the integral into multiple parts.
-
Understanding the Output: Make sure you understand the units of the result (usually square units).
Practical Applications and Examples
The calculation of the surface area of revolution has numerous real-world applications:
-
Engineering: Determining the surface area of components in manufacturing, such as curved pipes or containers. This is crucial for material estimation and cost calculations.
-
Architecture: Calculating the surface area of curved structures like domes or vaults, crucial for estimating material costs and structural analysis.
-
Physics: Calculating surface areas for problems involving heat transfer or fluid flow around curved surfaces.
-
Computer Graphics: Generating realistic 3D models, requiring accurate calculations of surface areas for rendering.
Conclusion
Calculating the surface area of revolution is a powerful mathematical tool with diverse practical applications. While the underlying principles involve calculus and integration, online calculators significantly streamline the process, making this complex calculation accessible to a broader audience. By understanding the methods, utilizing available calculators effectively, and troubleshooting potential problems, one can confidently apply this technique to various real-world scenarios. Remember to always double-check your inputs and understand the output of your calculations to ensure accuracy and meaningful results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Tall Is 170 Cm In Ft
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 22 Mm
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Much Is 90 Pounds In Kg
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 152 Cm In Feet
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Cm Is 20 Inches
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Area Of Surface Of Revolution Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
