Area Enclosed By Two Curves Calculator
Greels
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
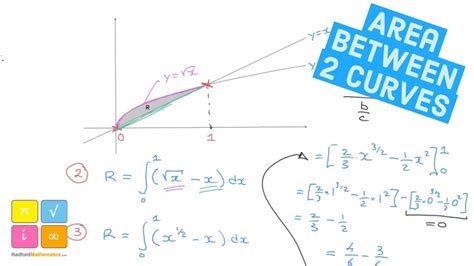
Table of Contents
Area Enclosed by Two Curves Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Calculating the area enclosed by two curves is a fundamental concept in calculus with wide-ranging applications in various fields like physics, engineering, and economics. While manual calculation can be tedious and prone to errors, especially with complex functions, numerous online calculators and software tools are available to simplify this process. This guide will delve into the theory behind calculating the area between curves, explore different methods, and demonstrate how to effectively use area enclosed by two curves calculators. We will also cover common challenges and provide tips for maximizing accuracy and efficiency.
Understanding the Fundamental Concept
The area enclosed by two curves, y = f(x) and y = g(x), within a specified interval [a, b] is determined by integrating the absolute difference between the two functions over that interval. This essentially involves finding the area of numerous infinitesimally thin vertical strips between the curves and summing them up. Visually, imagine slicing the region into many thin rectangles; the area of each rectangle is approximately its height (the difference between the functions at that x-value) multiplied by its width (dx), and the total area is the sum of these small areas.
Mathematically, the area A is represented as:
A = ∫<sub>a</sub><sup>b</sup> |f(x) - g(x)| dx
Where:
- f(x) and g(x) are the functions defining the upper and lower curves, respectively.
- a and b are the x-coordinates of the intersection points of the two curves, defining the limits of integration.
- |f(x) - g(x)| ensures that the area is always positive, regardless of which function is larger at a given point.
Determining the Limits of Integration
Identifying the correct limits of integration (a and b) is crucial for accurate area calculation. This usually involves finding the points where the two curves intersect. To find these points, set f(x) = g(x) and solve for x. The solutions to this equation will give you the x-coordinates of the intersection points, which define the interval [a, b]. If there are multiple intersection points, you might need to calculate the area in segments, integrating over each interval between consecutive intersection points.
Methods for Calculating the Area
Several approaches exist for calculating the area enclosed by two curves, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
1. Analytical Integration:
This method involves directly evaluating the definite integral using standard integration techniques. It requires a strong understanding of calculus and can become complex with intricate functions. However, it provides an exact solution, if the integral is solvable analytically.
2. Numerical Integration:
When analytical integration is difficult or impossible, numerical methods such as the trapezoidal rule, Simpson's rule, or Gaussian quadrature offer approximate solutions. These methods approximate the integral by dividing the area into smaller shapes (trapezoids, parabolas, or other functions) and summing their areas. The accuracy of the approximation increases with the number of segments used. Many area enclosed by two curves calculators utilize these numerical techniques behind the scenes.
3. Using an Area Enclosed by Two Curves Calculator:
Online calculators and software packages provide a user-friendly way to determine the area. These tools typically require you to input the functions f(x) and g(x) and the limits of integration (a and b). They then perform the necessary calculations, often employing numerical integration techniques, to provide the area.
How to Use an Area Enclosed by Two Curves Calculator Effectively
Using an online calculator typically involves these steps:
- Input the functions: Enter the equations of the two curves, f(x) and g(x), into the designated input fields. Use proper mathematical notation; ensure that the calculator understands the syntax.
- Specify the limits of integration: Enter the x-coordinates of the intersection points (a and b) that define the interval over which you are calculating the area. Some calculators might automatically detect the intersection points from the given functions.
- Select the calculation method: Some advanced calculators might offer choices regarding the numerical integration method (e.g., trapezoidal rule, Simpson's rule).
- Execute the calculation: Click the "Calculate" or equivalent button to initiate the computation.
- Interpret the results: The calculator will typically display the calculated area. Pay close attention to the units and ensure that the result is reasonable within the context of the problem.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting Tips
- Incorrect function input: Double-check your function input for typos and ensure you use the correct syntax.
- Incorrect limits of integration: Carefully determine the intersection points of the two curves and input the correct x-coordinates. Graphing the functions can help visualize the region and confirm the limits.
- Complex functions: For extremely complex functions, the calculator might struggle to provide an accurate result. Consider simplifying the functions if possible, or try using a different numerical integration method.
- Singularities or discontinuities: If the functions have singularities (points where they are undefined) or discontinuities within the interval [a, b], you might need to split the integral into multiple segments and calculate the area separately for each segment.
- Understanding the output: Ensure you understand what the calculator is outputting. Some might only give the numerical value, while others may provide a visual representation of the area.
Advanced Applications and Extensions
The concept of calculating the area between curves extends beyond simple functions. Here are some advanced applications:
- Volumes of solids of revolution: The area between curves can be used to find the volume generated when a region is revolved around an axis using techniques like the disk or washer method.
- Areas in polar coordinates: The same principles apply to areas enclosed by curves defined in polar coordinates, requiring the use of polar integration.
- Areas in three dimensions: In higher dimensions, the concept of area extends to surface integrals and calculating surface areas.
Conclusion
Calculating the area enclosed by two curves is a powerful tool with numerous applications. While manual calculation can be challenging, utilizing area enclosed by two curves calculators can streamline this process significantly, making it accessible to a broader audience. By understanding the fundamental principles, choosing the appropriate method, and being mindful of potential challenges, you can accurately and efficiently calculate the area between curves, unlocking the power of calculus for diverse applications. Remember to always double-check your inputs and consider the limitations of both analytical and numerical methods. The appropriate choice of method depends on the complexity of the functions and the desired level of accuracy. With the combination of theoretical knowledge and the practical assistance of online calculators, calculating the area enclosed by two curves becomes a straightforward and rewarding task.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Pounds Is 67 Kilograms
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Kilograms Is 155 Pounds
Mar 23, 2025
-
Greatest Common Factor Of Two Monomials Calculator
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 2 5 Meters
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Kilograms Is 140 Pounds
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Area Enclosed By Two Curves Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
