55 12 As A Mixed Number
Greels
May 02, 2025 · 4 min read
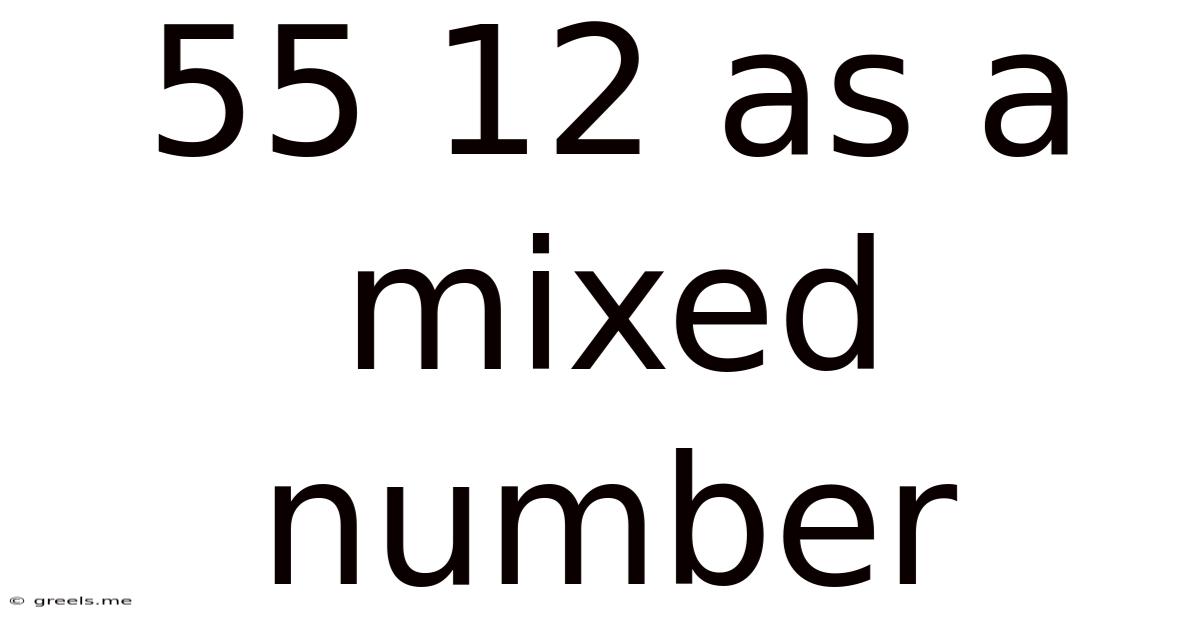
Table of Contents
55/12 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting improper fractions, like 55/12, into mixed numbers is a fundamental skill in arithmetic. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 55/12 into a mixed number but also delve into the underlying concepts, provide alternative methods, and offer practical applications. We'll also explore related topics to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify the terms:
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (top number) is greater than or equal to the denominator (bottom number). Examples include 55/12, 7/4, and 11/11.
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator smaller than the denominator. Examples include 4 ¾, 2 ⅓, and 1 ½.
The conversion process essentially involves determining how many times the denominator goes into the numerator and expressing the remainder as a fraction.
Converting 55/12 to a Mixed Number: The Standard Method
The most common method for converting an improper fraction to a mixed number involves division.
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator: Divide 55 by 12. This gives you a quotient (the whole number part of the mixed number) and a remainder.
55 ÷ 12 = 4 with a remainder of 7
-
The quotient becomes the whole number: The quotient, 4, is the whole number part of our mixed number.
-
The remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction: The remainder, 7, becomes the numerator of the fractional part.
-
The denominator remains the same: The denominator remains 12.
Therefore, 55/12 as a mixed number is 4 ⁷⁄₁₂.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 55 pizzas, and you want to divide them equally among 12 friends. Each friend would get 4 whole pizzas (4 x 12 = 48 pizzas). You'd have 7 pizzas left over (55 - 48 = 7). These 7 pizzas represent the remaining fraction, ⁷⁄₁₂. Thus, you have 4 whole pizzas and ⁷⁄₁₂ of a pizza left, representing 4 ⁷⁄₁₂.
Alternative Methods for Conversion
While the standard division method is straightforward, let's explore some alternative approaches:
Method 1: Repeated Subtraction
Repeatedly subtract the denominator from the numerator until you get a number less than the denominator. The number of times you subtracted is your whole number, and the remainder is your new numerator.
55 - 12 = 43 43 - 12 = 31 31 - 12 = 19 19 - 12 = 7
We subtracted 12 four times, so our whole number is 4. The remainder is 7, giving us 4 ⁷⁄₁₂.
Method 2: Using Equivalent Fractions (Less Efficient for Larger Numbers)
This method is less practical for larger numbers like 55/12 but can be helpful for smaller improper fractions. You find an equivalent fraction with a numerator that's a multiple of the denominator. This requires a bit of trial and error. It's not the most efficient for larger numbers but demonstrates an alternative concept.
Applications of Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers is crucial in various real-world scenarios:
-
Measurement: Imagine measuring ingredients for a recipe. If a recipe calls for 55/12 cups of flour, it's much easier to understand and measure 4 ⁷⁄₁₂ cups.
-
Time: Dividing time intervals often results in improper fractions. For example, 55/12 hours is more easily understood as 4 hours and 35 minutes (7/12 of an hour is 35 minutes).
-
Geometry and Construction: Many geometric calculations involve fractions. Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers simplifies these calculations and makes them more intuitive.
-
Data Analysis: When dealing with fractional data, expressing results as mixed numbers can enhance clarity and understanding.
Simplifying Mixed Numbers
While 4 ⁷⁄₁₂ is already in its simplest form (because 7 and 12 share no common factors other than 1), it's important to understand how to simplify mixed numbers if necessary. If the fractional part can be reduced, always simplify it. For example, if you had 4 ⁶⁄₁₂, you'd simplify the fraction to ½, resulting in 4 ½.
Converting Mixed Numbers Back to Improper Fractions
It's equally important to understand the reverse process. To convert a mixed number back to an improper fraction:
-
Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 4 x 12 = 48
-
Add the numerator: 48 + 7 = 55
-
Keep the same denominator: The denominator remains 12.
Therefore, 4 ⁷⁄₁₂ converts back to 55/12.
Practice Problems
To reinforce your understanding, try converting these improper fractions to mixed numbers:
- 23/5
- 37/8
- 61/15
- 95/11
Solutions:
- 23/5 = 4 ⅗
- 37/8 = 4 ⅝
- 61/15 = 4 ⅛
- 95/11 = 8 ⅞
Conclusion
Converting 55/12 to the mixed number 4 ⁷⁄₁₂ is a straightforward process, essential for various mathematical applications. Mastering this conversion, along with understanding the related concepts and alternative methods, will significantly improve your arithmetic skills and problem-solving abilities. Remember to always check for simplification opportunities and practice regularly to enhance your fluency. The ability to seamlessly move between improper fractions and mixed numbers will serve you well in numerous academic and real-world situations.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 55 12 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.